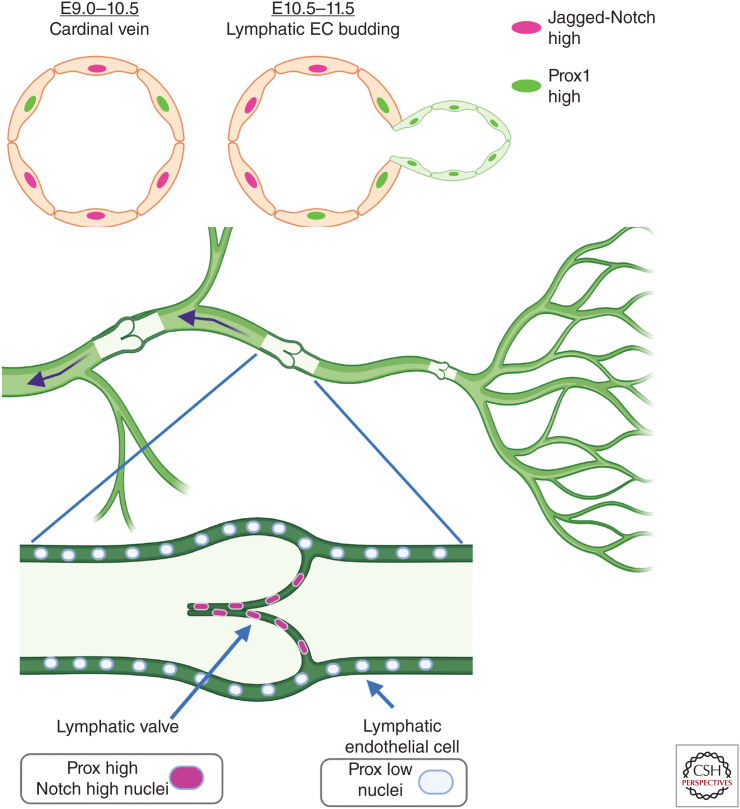
Figure 3.
Acquisition of lymphatic endothelial and lymphatic valve cell fates. (Top) During murine embryonic development, Prox1-expressing cells form in the cardinal vein (right side on schematized vein) and bud to form a sprout that initiates lymphatic development. Notch1 and Jagged1-expressing cells are located at the opposite side of the vein from Prox1-expressing cells and loss-of-function experiments demonstrate that Notch suppresses Prox1 expression, assuring proper lymphatic development. (Bottom) Lymphatic vasculature consists of capillaries that collect fluid, which is directed through lymphatic ducts containing valves that assure unidirectional flow. During initial development of lymphatic valves, lymphatic endothelial cells (ECs) express high levels of Prox1 and have high Notch signaling, and loss of Notch1 or canonical Notch signaling prevents proper lymphatic valve development.