FIGURE 4.
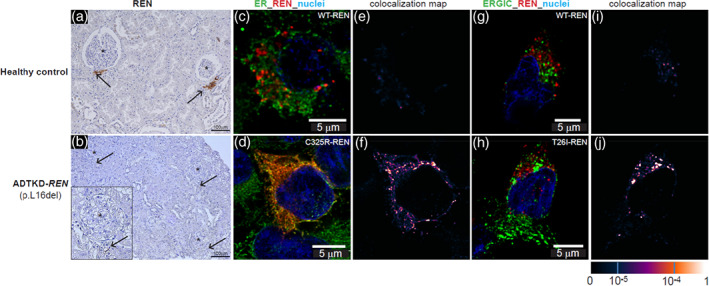
Immunostaining for renin (REN). Immunostaining of previously obtained biopsies can help determine if a variant of uncertain significance is pathogenic. (a) Horseradish peroxidase staining for renin occurring in the juxtaglomerular apparatus (black arrows) in control kidney. (b) Minimal staining of renin is found (black arrows) in the ADTKD‐REN patient kidney. (c) Immunofluorescence staining for wild type renin (WT‐REN) in transiently transfected HEK293 cells together with an ER marker (PDI). There is no colocalization identified (e). In contrast, in (d) immunostaining of the HEK293 cells transiently transfected with the p.Cys325Arg‐REN mutation (mature renin) shows deposition of renin within the ER, as evidenced by colocalization (f). (h) HEK293 cells transiently transfected with the p.Thr26Ile‐REN mutation (prosegment) immunoflourescently stained with an antibody to REN (red) and the endoplasmic reticulum‐Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC). In the WT‐REN (g) there is no colocalization (i). In contrast, in the p.Thr26Ile‐REN mutation, there is abundant deposition of REN within the cell (h), colocalizing with the ERGIC (j)
