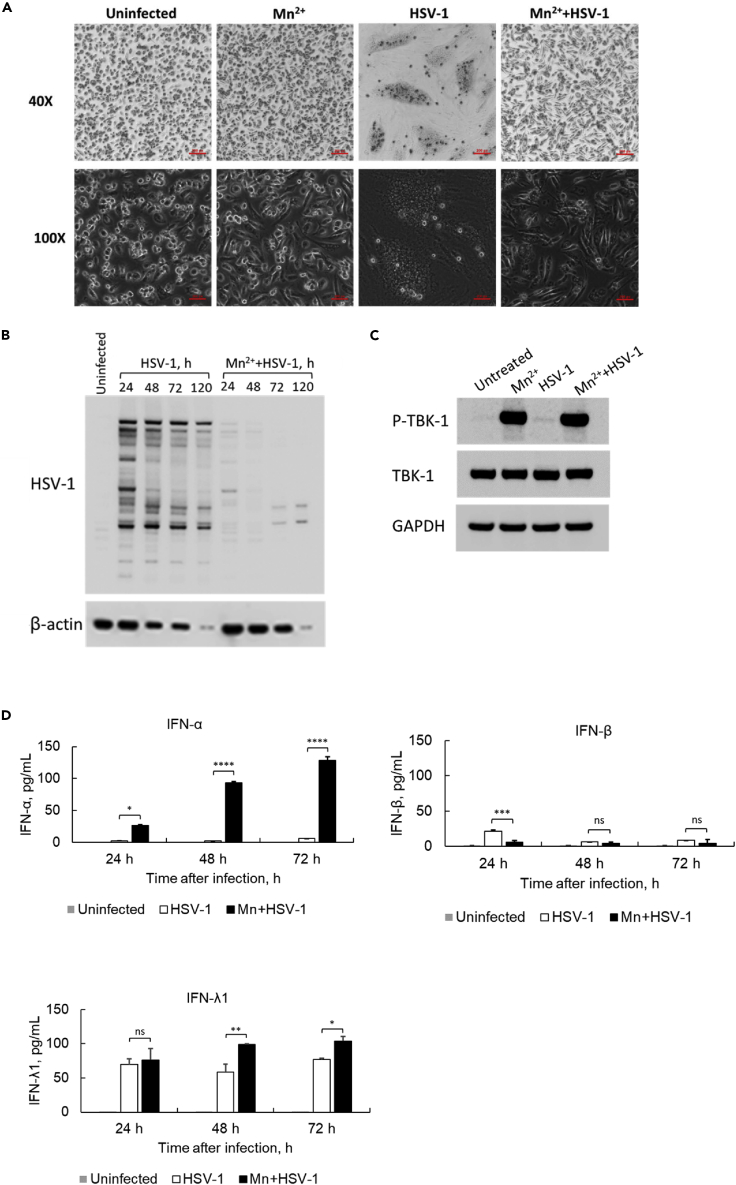
Figure 5.
Mn treatment protects macrophages from HSV-1 McKrae infection
(A) The effect of pretreatment with Mn2+ on morphological changes in human primary macrophages infected with the HSV-1 McKrae strain. Human macrophages were pretreated with Mn2+, then mock-infected (uninfected) or infected with the HSV-1 McKrae strain at an MOI of 1. Cells were observed under a phase-contrast microscope at 40× and 100× magnification 24 h after HSV-1 infection. Scale bar = 200 μM. One representative experiment of at least three independent experiments is shown.
(B) Human macrophages were treated with or without Mn2+, then infected with HSV-1 McKrae at an MOI of 1. The total cell lysate was collected at different time points after infection, and WB was performed using anti-HSV-1 and anti-β-actin antibodies. The untreated sample was collected at 48 h after cell seeding. One representative experiment of at least three independent experiments is shown.
(C) Macrophages were treated with or without Mn2+, then infected with HSV-1 McKrae at an MOI of 1. The total cell lysate was collected at 24 h after infection, and WB was performed using anti-p-TBK1, anti-TBK1 and anti-GAPDH antibodies. One representative experiment of at least three independent experiments is shown.
(D) Cell culture supernatants were collected at 24, 48, and 72 h after virus infection. The protein expression of IFN-α, IFN-β, and IFN-λ1 was detected by ELISA. One representative experiment of at least three independent experiments is shown. And each was done as duplicate. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 2). Not significant (ns) p> 0.05, ∗p< 0.05, ∗∗p< 0.01, ∗∗∗p< 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p< 0.0001 (One-way ANOVA) were indicated in the figures where the IFN protein expression level was compared between HSV-1 infected cells and Mn2+/HSV-1 infected cells.