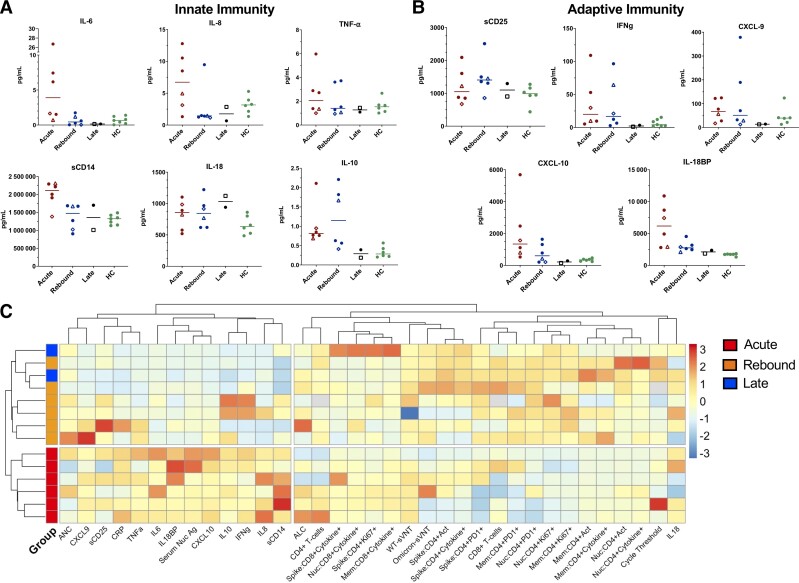
Figure 5.
Innate and adaptive biomarkers across study groups compared with healthy controls and heat map of data from study participants. Lines represent medians and points represent individual results across the acute, rebound, and late presentation coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) clinical groups compared with healthy control population (HC). Healthy controls consisted of 5 women and 2 men with a median age of 59 years (range, 45–66). These samples were unmatched and are included to provide a baseline range for these biomarkers in an otherwise healthy population. The 2 longitudinal COVID-19 rebound patients are identified by an open diamond (patient 1) and open triangle (patient 2). The open square represents the COVID-19 rebound patient who did not receive nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (NMV-r). A, Innate biomarkers (IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, CXCL-10, sCD14, and IL-18BP) classically increased in acute COVID-19 are downtrending at time of rebound. B, Adaptive biomarkers representing T-cell activation (IFN-γ, CXCL-9, sCD25) were stable or increasing at rebound consistent with a developing T-cell response. C, Comprehensive heat map with unsupervised clustering of variables including clinical laboratory tests, virologic measurements, biomarkers, and profiling of adaptive responses identified that all patients with rebound COVID-19 after NMV-r form a unique cluster distinct from those with acute infection. The late presenting patient and rebound patient without NMV-r cluster with the other rebound COVID-19 patients. Analysis performed in R using the pheatmap package. One patient with acute COVID-19 and 1 rebound patient without NMV-r (both with BA.5) were excluded from the heat map due to missing biomarker data. Abbreviations: CXCL-10, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10; HC, healthy controls; IFN-γ, interferon γ; IL, interleukin; IL-18BP, interleukin 18 binding protein; sCD25, soluble CD25; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α.