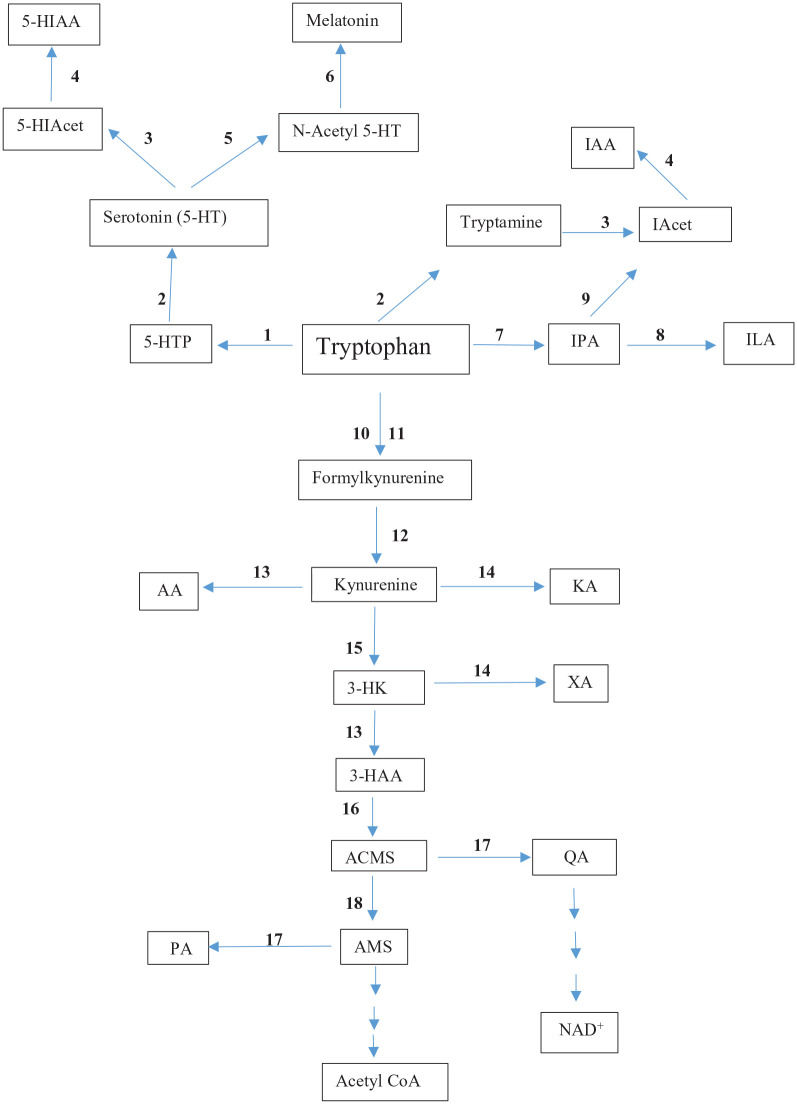
Figure 1.
The tryptophan degradative pathways.
Abbreviations: Acet, acetaldehyde; ACMS, 2-Amino-3-carboxymuconic acid-6-semialdehyde: also known as acroleyl aminofumarate, AMS, 2-Aminomuconic acid -6-semialdehyde; AA, anthranilic acid; 3-HAA, 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid; 5-HIAcet, 5-hydroxyindoleacetaldehyde; 5-HIAA, 3-hydroxyindoleacetic acid; 3-HK, 3-hydroxykynurenine; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine or serotonin; 5-HTP, 5-hydroxytryptophan; IAcet, indole acetaldehyde; IAA, indol-3-ylacetic acid; ILA, indol-3-yllactic acid; IPA, indol-3-ylpyruvic acid; KA, kynurenic acid; PA, picolinic acid; QA, quinolinic acid; XA, xanthurenic acid.
Bold numbers represent enzymes of the different pathways, as follows: 1 (tryptophan hydroxylase); 2 (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase); 3 monoamine oxidase); 4 (aldehyde dehydrogenase); 5 (alkyl amine N-acetyl transferase); 6 (hydroxyindole o-methyl transferase); 7 (tryptophan aminotransferase); 8 (indole lactate dehydrogenase); 9 (indole pyruvate decarboxylase); 10 (tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase); 11 (indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase); 12 (N′-formylkynurenine formamidase); 13 (kynureninase); 14 (kynurenine aminotransferase); 15 (kynurenine monooxygenase: also known as kynurenine hydroxylase); 16 (3-hydroxyanthranilic acid 34-dioxygenase); 17 (non-enzymic cyclisation); 18 (2-Amino-3-carboxymuconic acid-6-semialdehyde decarboxylase (ACMSD: also known as picolinate carboxylase).