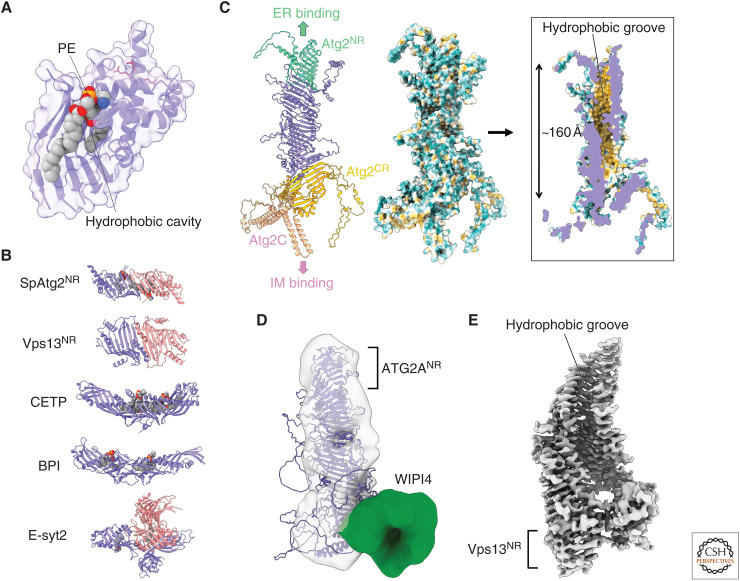
Figure 2.
Structural basis of Atg2-mediated lipid transfer. (A) Crystal structure of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)-bound SpAtg2NR (PDB 6A9J). Basic residues responsible for the membrane tethering activity of Atg2 are shown with red stick models. All structural models in this manuscript were prepared using PyMOL. (B) Capsule-like structures found in various lipid transfer proteins: SpAtg2NR, the amino-terminal region of Vps13 (Vps13NR; PDB 6CBC), cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP; PDB 2OBD), bactericidal permeability-increasing protein (BPI; PDB 1BP1), and extended synaptotagmin 2 (E-syt2; PDB 4P42). Monomers in capsule-like structures are colored in slate or salmon. Lipids bound to capsule-like structures are displayed as a sphere model. (C) AlphaFold structure of Atg2. (Left) Ribbon model of Atg2 whose domains are colored differently. (Middle and right) Outer and inner surface model of Atg2 in which hydrophobicity is shown in Kyte–Doolittle scale. The most hydrophobic region is colored in orange-red. (D) Fitting of the AlphaFold structure of ATG2A to the electron microscopy (EM) density map of the ATG2A-WIPI4 complex (EMD-8899). (E) Cryo-EM density map of the amino-terminal fragment of Chaetomium thermophilum VPS13 (EMD-21113).