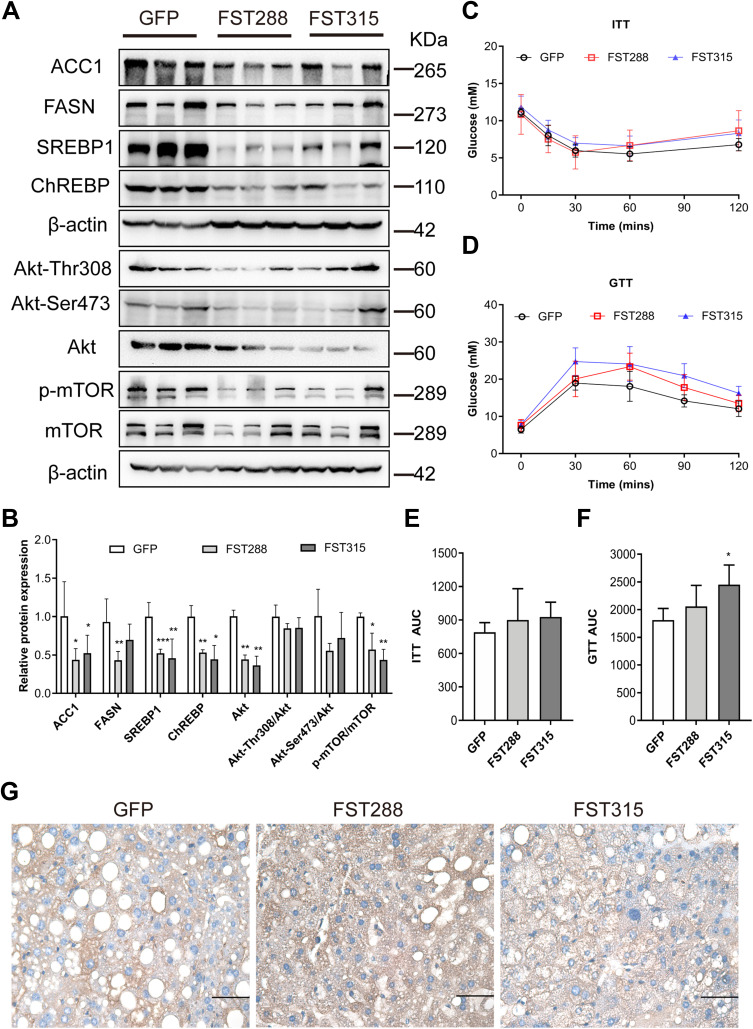
Figure 8.
FST overexpression inhibited lipid synthesis and Akt/mTOR pathway in HFD mice. (A and B) The protein expression and analysis results of ACC1, FASN, SREBP1, ChREBP, Akt, Akt-Thr308, Akt-Ser473, p-mTOR, and mTOR in the control (treated with an AAV vector encoding GFP) and FST-overexpressing (treated with an AAV vector encoding FST288 and FST315) HFD mice. β-actin was used as a loading control. (C and D) GTT and ITT results in the control and FST-overexpressing HFD mice. (E and F) AUC for GTT and ITT. (G) Immunohistochemical staining of hepatic FST in the control and FST-overexpressing HFD mice (400×, scale bar: 50 µm).
Notes: n= 5. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001 vs GFP group.
Abbreviations: FST, follistatin; SREBP1, sterol regulatory element-binding protein1; ChREBP, carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein; ACC1, acetyl-CoA carboxylase1; FASN, fatty acid synthase; Akt, protein kinase B; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; GTT, glucose tolerance test; ITT, insulin tolerance test; AUC, area under the curve; AAV, adeno-associated virus.