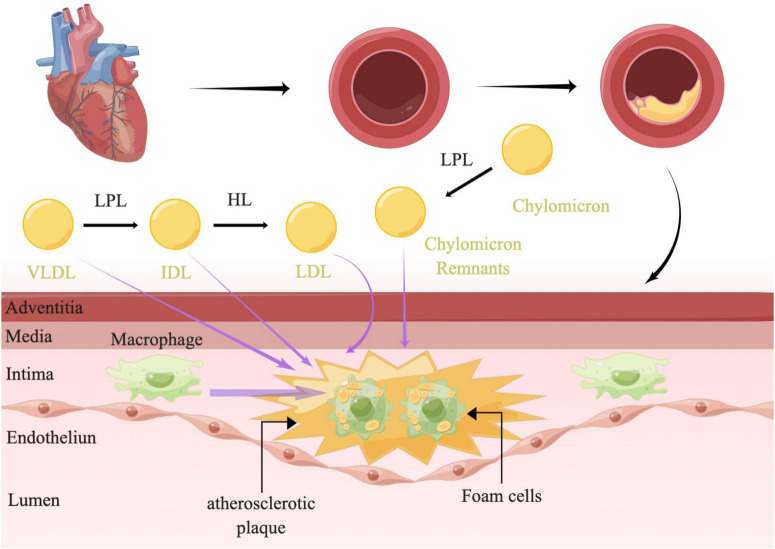
FIGURE 3.
The mechanism of atherosclerosis. LPL along the capillary lumen surface hydrolyzed VLDL, resulting in VLDL remnants/IDL particles and lipolysis products. The IDL particles were further catabolized into LDL by HL. LPL could also hydrolyzed chylomicrons to produce chylomicron remnants. TRLs and their remnants readily penetrate the arterial wall and can be taken up by scavenger receptors on macrophages directly without oxidative modification, leading to formation of foam cells and atherosclerotic plaque development. TRLs, triglyceride-rich lipoproteins; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; HL, hepatic lipase; VLDL, very-low-density lipoprotein; IDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; RC, remnant cholesterol.