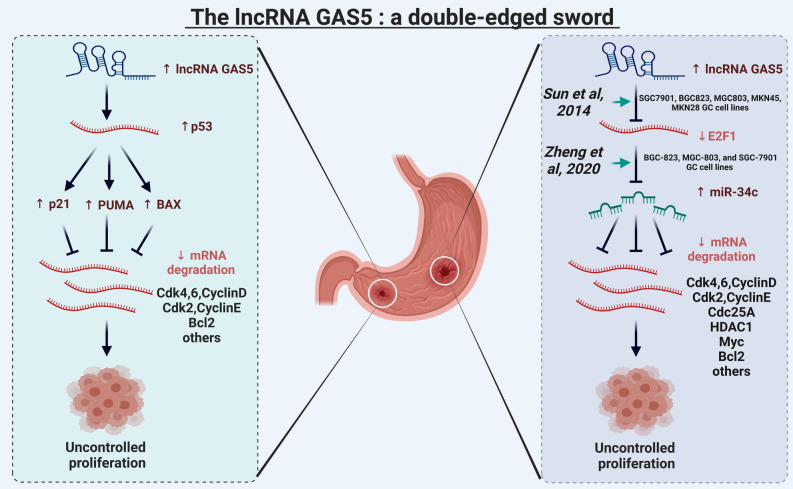
Figure 4.
lncRNA-GAS5: a double-edged sword in tumor growth and proliferation in GC. On the left (highlighted in the green box), p53 was directly activated by lncRNA-GAS5 in GC45. Once p53 expression is activated, it may induce p2168, PUMA/BAX68. Although, the expression of p21 does not depend on the p53 functionality in GC7,8. Despite this fact, activated p21 and PUMA/BAX, which directly inhibit the expression of the CDK4/6-CyclinD and CDK2-CyclinE, Cdc25A, Bcl2, and others and induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis at the G1/S checkpoint. On the right (highlighted in the purple box), the novel tumor suppressor mechanism of lncRNA-GAS5 is captured by the Boolean network. Overexpression of lncRNA-GAS5 directly inhibits E2F1 expression15, which triggers miR-34c expression3. Then, overexpression of miR-34c directly targets the CDK4/6-CyclinD and CDK2-CyclinE, Cdc25A, HDAC1, Myc, Sirt1, Mdm2, and Bcl2, see the review by Xiong et al.67. Targeting these molecules activates cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death at the G1/S checkpoint in GC. Thus, lncRNA-GAS5/miR-34c axis inhibits tumor growth and uncontrolled proliferation in GC. Consequently, p53-dependent or independently of p53, lncRNA-GAS5 can prevent tumor progression and cell proliferation in GC.