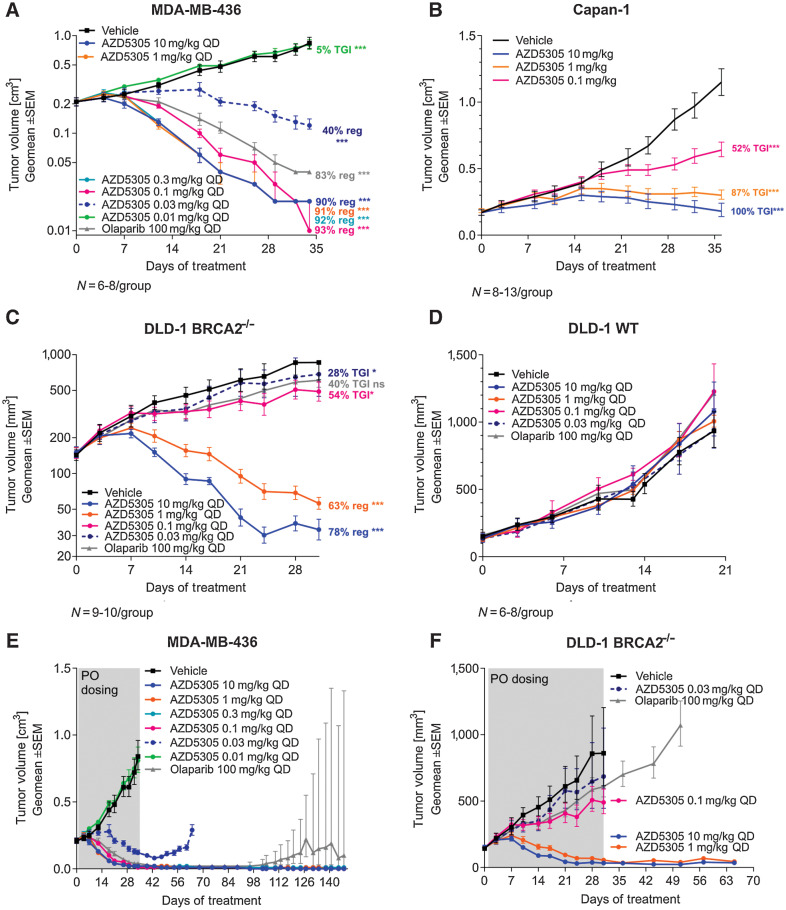
Figure 3.
Efficacy of AZD5305 in BRCAm xenograft tumor models. Antitumor efficacy of AZD5305 dose–responses in MDA-MB-436 BRCA1m TNBC xenograft (A), in Capan-1 BRCA2m pancreatic cancer xenograft (B), and in isogenic xenograft tumor models DLD-1 BRCA2−/− (C) and DLD-1 WT (D). Mice were dosed with indicated doses of AZD5305 or 100 mg/kg olaparib once daily orally for 35 (A, B), 31 (C), or 20 (D) days. E and F, In experiments from A and C, treatment was withdrawn as indicated and tumors were monitored for the regrowth. Graphs depict geomean tumor volume ±SEM and percent tumor growth inhibition (TGI) or regression (reg). Statistical significance was evaluated compared with the vehicle group using a one-tailed t test (*, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001).