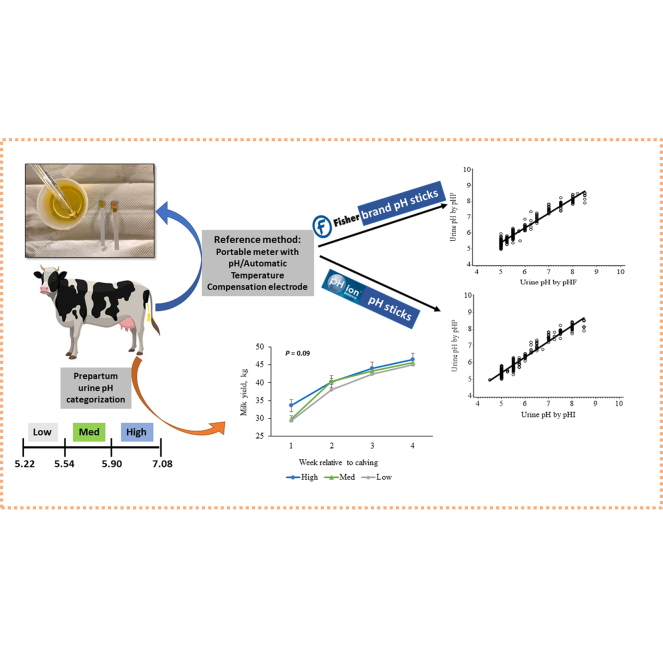
Summary: Acidified diets prepartum are utilized in dairy cows to decrease the likelihood of hypocalcemia; however, the effect of the extent of acidification on cow performance is still debated. Our objective was to validate the accuracy of 2 pH strips to measure urine pH (categorized as low, medium, or high) in dairy cows consuming an acidified diet prepartum and the association of urine pH with production performance. We determined that both pH strips are an accurate and affordable method to determine urine pH. Additionally, varying urine pH was not associated with dry matter intake when cows consumed an acidified diet; however, milk yield was moderately affected during week 1 postpartum when average urine pH prepartum was <5.67.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.