Figure 1.
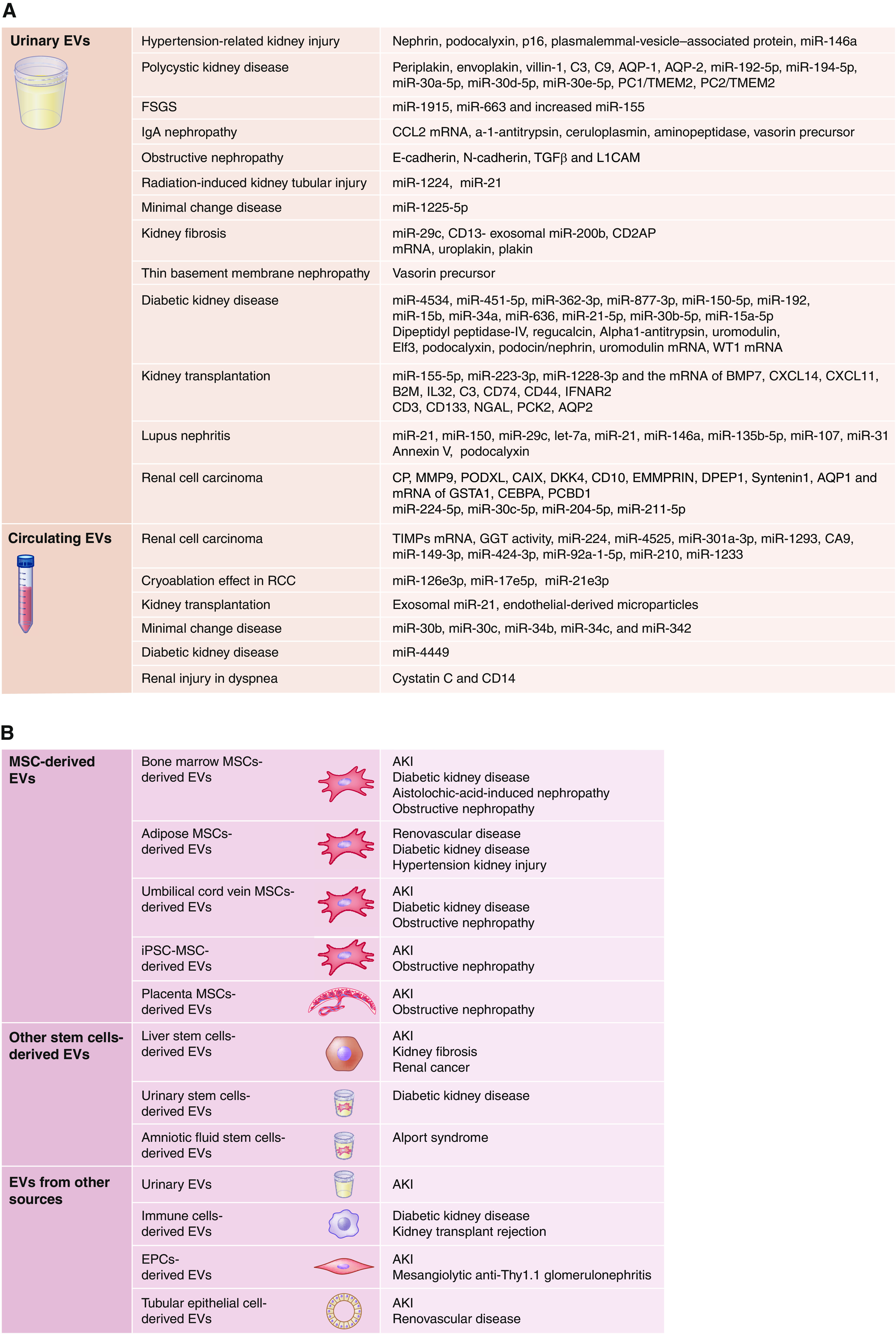
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are ubiquitous diagnostic and therapeutic tools in kidney diseases. (A) EV-based biomarkers of kidney diseases include urinary and circulating EVs. Urinary EVs have been widely applied to detect kidney diseases or injury, including diabetic kidney disease (DKD), kidney transplantation, lupus nephritis, renal cell carcinoma (RCC), hypertension, polycystic kidney disease, FSGS, IgA nephropathy, obstructive nephropathy, radiation-induced kidney injury, minimal change kidney disease, kidney fibrosis, and basement membrane nephropathy. Circulating EVs have been studied in fewer diseases (including RCC, kidney transplantation, minimal change kidney disease, DKD, and renal injury in dyspnea). (B) EVs harvested from different tissues can serve as therapeutic tools in kidney diseases. Proposed sources for EVs include tissue mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), tubular epithelial cells, urine, and human placenta. B2M, beta-2 microglobulin; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; CAIX, carbonic anhydrase IX; CD, cluster of differentiation; CEBPA, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha; CP, ceruloplasmin; CXCL, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; DDK, dickkopf-related protein; DPEP, dipeptidase; EMMRIN, extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer; GGT, γ-glutamyltransferase; GSTA, glutathione S-transferase A; IFNAR, interferon-α/β receptor; IgA, immunoglobulin A; IL, interleukin; L1CAM, L1 cell adhesion molecule; miR, microRNA; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NGAL, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; PC, polycystin; PCBD, pterin-4-alpha-carbinolamine dehydratase; PCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; PODXL, podocalyxin-like protein; RVD, renovascular disease; TIMPs, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; TMEM, transmembrane protein.
