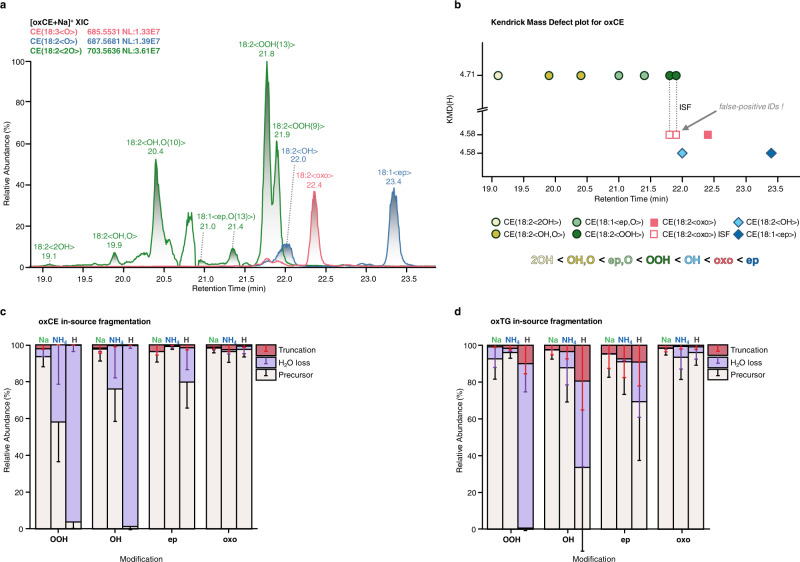
Fig. 3. LC-MS/MS coupling and retention time (RT) mapping facilitate resolution of isomeric oxidized lipids and allow to correct for in-source fragmentation (ISF).
Isomeric oxidized lipids can be successfully resolved by RPC, as illustrated here for mono- (CE(18:3<O>) in red and CE(18:2<O>) in blue) and dioxygenated (CE(18:2<2O>) in green) oxCE lipids (a). RT mapping using KMD(H) plots allows visual inspection of isomer-specific elution order as well as identification of false positive annotation due to the ISF (b). The extent of ISF for oxCE (c) and oxTG (d) lipids was shown to be ionization- and modification type-specific. ISF was calculated based on the parent and product peak areas using the formula . Relative abundances of ISF-derived species (truncation and water loss) for oxCE (c) and oxTG (d) represent (mean ± SD) values calculated for 10 species. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.