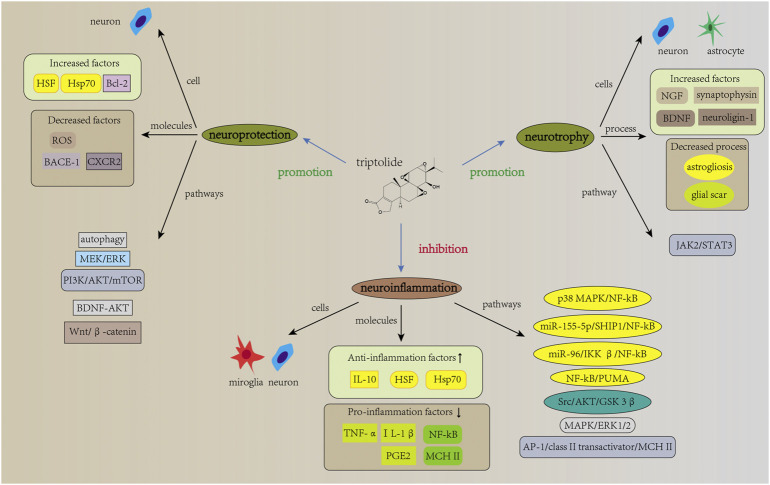
FIGURE 2.
Mechanisms of action of triptolide in neurological diseases. The mechanisms of action of triptolide in neurological diseases involves neuroinflammation, neurotrophic effects, and other neuroprotective effects. It attenuates neuroinflammation and regulate inflammation levels in microglia and neuron, as evidenced by increased expression of anti-inflammatory factors and decreased expression of pro-inflammatory factors. Signaling pathways such as NF-kB are involved in this regulation. In addition, current studies have reported neurotrophic effects of triptolide for neurological diseases. Triptolide increases the expression levels of NGF, synaptophysin, neuroligin-1, and BDNF mRNA, and it also inhibits astrogliosis and excessive glial scar, which is associated with the regulation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Furthermore, triptolide can act directly on neurons and thus exert neuroprotective effects by affecting other signaling pathways such as autophagy and apoptosis.