Figure 1.
Expression profile of gmap-1, gmap-2 and gmap-3 in C. elegans
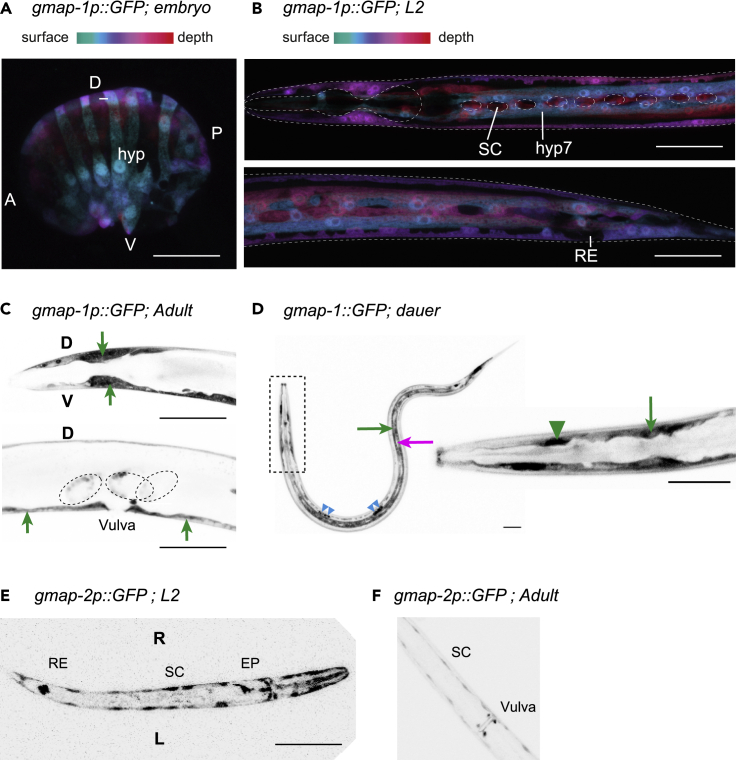
The expression pattern of gmap-1 was determined using a GFP transcriptional reporter strain bearing a [gmap-1p::SL2 GFP] transgene.
(A) In comma stage embryo, GFP expression was observed in the hypodermal precursor cells (hyp) before ventral closure. GFP fluorescence is reported in 3D using depth color-coded projection. Scale bar = 50 μm. A: anterior, P: posterior, V: ventral, D: dorsal.
(B) During the second larval stage, GFP expression was observed in the hypodermis syncytium (hyp7), in hypodermal cells of the head and tail, but not in the rectal epithelium (RE) or seam cells (SC). GFP fluorescence is reported in 3D using depth color-coded projection. Scale bar = 100 μm.
(C) In adults, GFP expression was observed in the hypodermis of the head (green arrows) and in the hyp7 hypodermal syncytium surrounding the vulva (green arrow) but not in the vulval epithelium itself. It was also observed in embryos, prior to egg laying (scattered circle). Scale bar = 100 μm.
(D) We observed GFP was strongly expressed in dauer hypodermis (green arrows) but not in seam cells (magenta arrow). It was observed in unidentified head’s glia (green arrowhead), as well as in coelomocytes (blue arrowheads). Scale bar = 100 μm.
(E and F) The expression pattern of the gmap-2, gmap-3 operon was determined using a transcriptional reporter strain bearing a [gmap-2p::GFP] transgene: (E) GFP expression was observed in the seam cells (SC), the excretory pore (EP) and the rectal epithelium (RE) of the L1 stage (F) GFP expression was observed in the seam cells and vulval cells of adults. Scale bar = 100 μm. Images are representative of over 30 animals observed over 2 or 3 independent sampling.