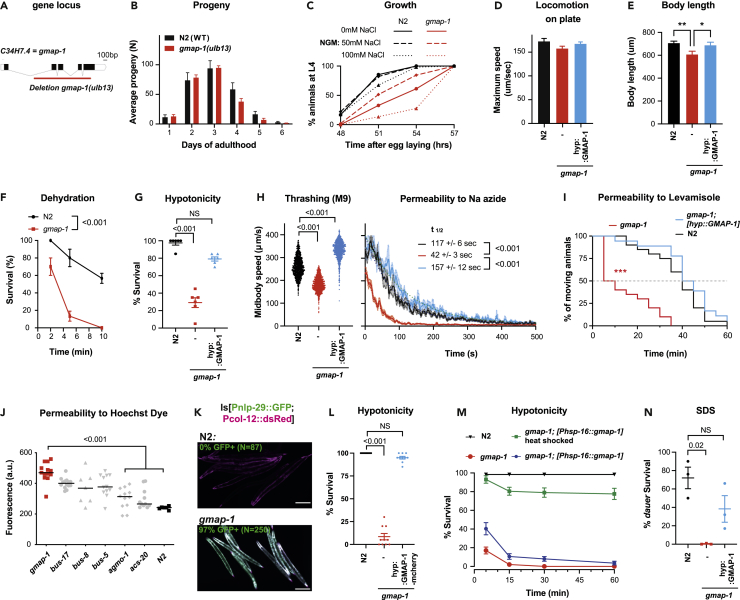
Figure 2.
gmap-1 deletion increases cuticular permeability
(A) Schematic representation of the gmap-1 gene and the localization of the 1515 bp deleted by CRISPR in gmap-1(ulb-13).
(B) Analysis of the progeny produced by N2 and gmap-1 over the first 6 days of adulthood.
(C) The percentage of individuals reaching L4 stage determined 48 h after an egg laying window for ∼70 N2 and gmap-1. The animals were grown at 20°C in presence of fresh bacteria either on regular NGM plates (50nM NaCl) or at indicated NaCl concentrations.
(D) The maximum forward speed of N2 and gmap-1 determined on NGM plates in presence of OP50 bacteria (N = 60 across 3 replicates; One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnet’s comparison).
(E) Body length measured in young adults 3 h post L4 stage for N2, gmap-1, and gmap-1(ulb13) carrying Ex[agmo-1p::gmap-1SL2GFP] (N = 60 across 3 replicates; One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnet’s comparison, ∗:p value <0.05; ∗∗:p value <0.01).
(F) Survival to dehydration measured for adult worms after 5 min of contact to dried 2% agar pad covered with mineral oil (N = 30 across 3 replicates; 2-way RM ANOVA with Geisser correction).
(G) Survival to hypotonicity measured for adult worms after 15 min exposure to deionized water (N = 200 across 10 replicates). Survival was measured for N2, gmap-1(ulb13) mutants, and gmap-1(ulb13) rescued in the hypodermis by the expression of Ex[agmo-1p::gmap-1SL2GFP]. One-way ANOVA followed by Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’ correction for multiple comparisons.
(H) Thrashing speed in M9 buffer was measured for N2, gmap-1(ulb13) mutants, and gmap-1(ulb13) carrying Ex[agmo-1p::gmap-1SL2GFP]. The induction of paralysis by 5 mM sodium azide was measured over 10 min. The half-life is calculated by one-phase decay non-linear fit. (N = ≥80 across 5-6 replicates per group; One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnet’s comparison).
(I) The percentage of individuals paralyzed in presence of 0.4 mM Levamisole was measured over 1 h for N2, gmap-1(ulb13) mutants, and gmap-1(ulb13) carrying Ex[agmo-1p::gmap-1SL2GFP]. (N = 80 across 4 replicates, Log rank p value compared to N2, ∗∗∗:p value <0.001).
(J) The median cuticular permeability to Hoechst 33342 was measured for 20 individuals of the indicated genotypes. Fluorescence was quantified in the head after 30 min exposure to Hoechst 33342. One-way ANOVA followed by Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’ correction for multiple comparisons.
(K) A transcriptional reporter strain carrying Is[nlp-29p::GFP; col-12p::DsRed] was crossed with gmap-1 mutants and N2 controls and grown on regular NGM plates + OP50 E. coli. Images are representative of the induction of nlp-29p::GFP, observed in 94.4% (N = 250) of gmap-1(ulb13) but in none of the N2 controls (N = 87). Scale bar = 200 μm.
(L) Hypodermal expression of GMAP-1-mcherry was assessed for its ability to rescue hypersensitivity to deionized water of gmap-1 mutants. Survival in deionized water was quantified for N2, gmap-1 and in a strain co-expressing cytoplasmic mEGFP and GMAP-1-mCherry under an hypodermis promoter [agmo-1p::eGFP; agmo-1p::gmap-1-mCherry]. One-way ANOVA followed by Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’ correction for multiple comparisons.
(M) Acute expression of GMAP-1mCherry in adults was assessed for its ability to rescue hypersensitivity to deionized water of gmap-1 mutants. Survival in deionized water was quantified for N2, gmap-1 and in a strain expressing GMAP-1-mCherry under a heat-shock promoter [phsp-16::gmap-1-mCherry] maintained at 15°C and exposed to 33°C for 5 min at late L4 stage. As negative control, the [phsp-16::gmap-1-mCherry] strain was maintained at 15°C, instead. One-way ANOVA followed by Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’ correction for multiple comparisons.
(N) Survival after 30 min of exposure to 1% SDS was measured for 60 dauers in 3 replicates. dauer survival was measured for N2, gmap-1(ulb13) mutants, and gmap-1(ulb13) carrying Ex[agmo-1p::gmap-1SL2GFP]. One-way ANOVA followed by Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’ correction for multiple comparisons. All data are represented as Mean +/− SEM.