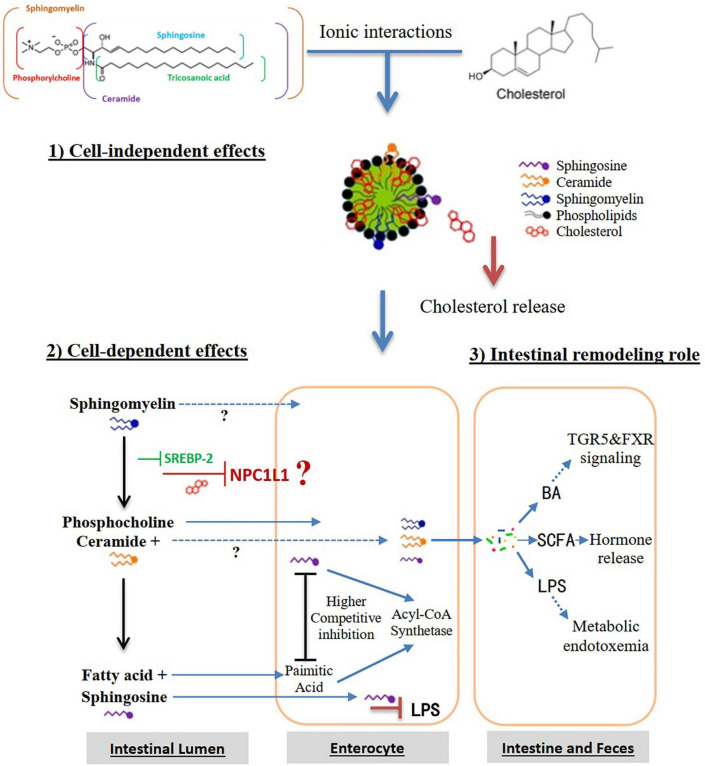
FIGURE 4.
Hypothesis that dietary sphingomyelin inhibits the intestinal cholesterol absorption pathways. Alk-SMase, alkaline SMase; SREBP-2, sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2; NPC1L1, Niemann-Pick-Like Protein 1; N-CDase, neutral ceramidase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; BA, bile acid; TGR5, Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; SCFA, short-chain fatty acids.