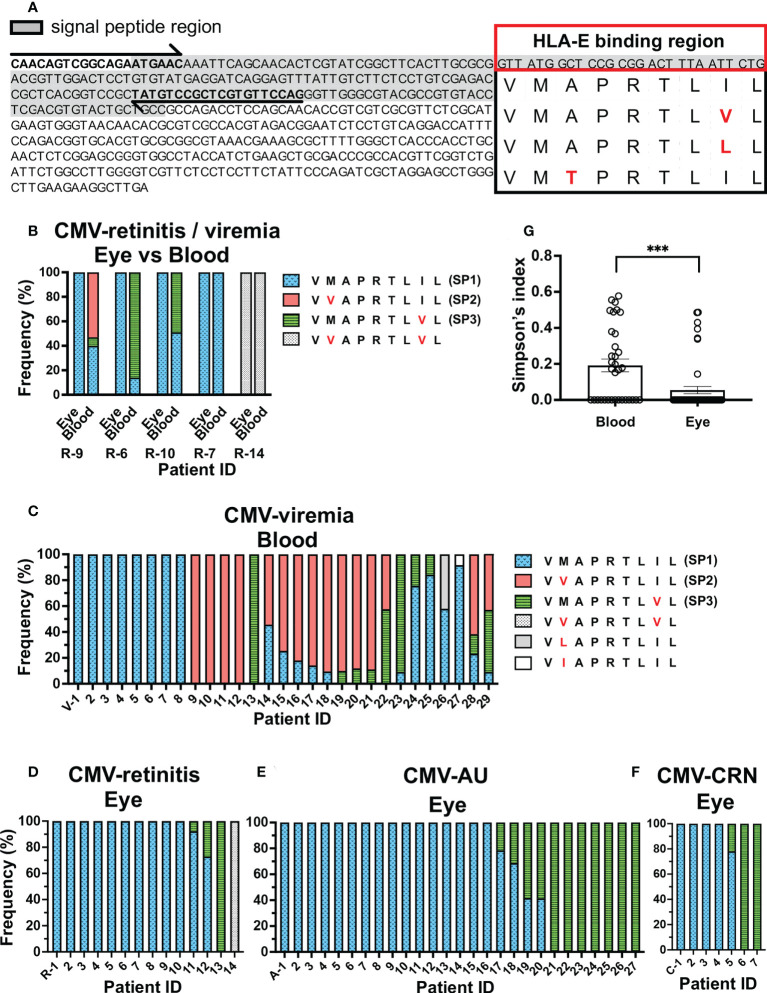
Figure 1.
Repertoire of CMV UL40 signal peptide sequences in ocular fluids is distinct from that in peripheral blood. (A) Schematic of strategy for detecting UL40 signal sequence region. Full-length UL40 genetic sequence and the upstream region are shown with primer positions (arrows). Signal peptide region is shaded, and representative HLA-E-binding peptide sequences from previous studies are shown (24, 34, 35). (B) Distribution of UL40-encoding signal peptide sequences from five CMV-viremia patients with CMV-retinitis. (C–F) Distributions of HCMV UL40-encoding signal peptide sequences identified in peripheral blood of 29 CMV-viremia patients (C) and intraocular fluids of 14 CMV-retinitis (D), 27 CMV-AU (E), and 7 CMV-CRN patients (F). X axis is annotated with patient IDs. V-, viremia; R-, retinitis; A-, AU; C-, CRN (G) Comparison of UL40 signal peptide sequence diversity between the blood and intraocular fluid using Simpson’s diversity index. Two-tailed t-test was used for statistical analysis. ***P = 0.0006.