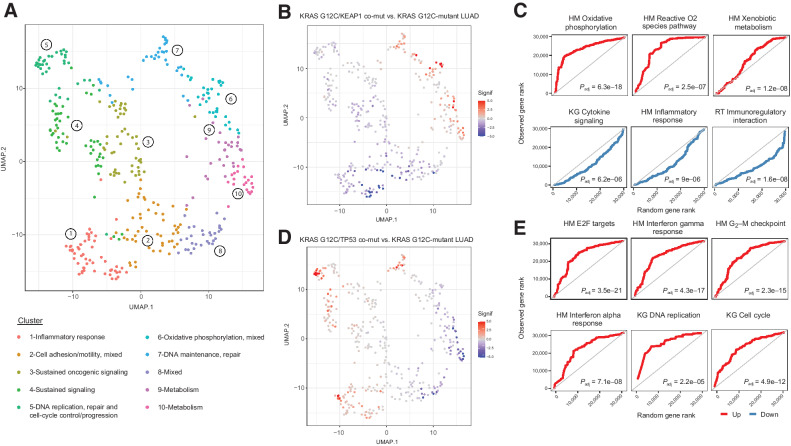
Figure 6.
Differential expression profiles driven by KRAS G12C comutation status in LUADs. Comutation-driven GSEA leveraging transcriptomic profiles from RNA sequencing revealed marked differences in gene expression programs depending on KRAS G12C comutations. A, Normalized enrichment scores from GSEA in KRAS G12C-mutant LUADs harboring different comutations were used as an input for UMAP dimensionality reduction, which revealed convergence of gene sets in distinct clusters related to immune/inflammatory response, metabolism, sustained/mitogenic signaling, oxidative phosphorylation, apoptosis, DNA maintenance, replication and repair, and cell-cycle progression. B and C,KRAS G12C/KEAP1 comutant LUADs showed a downregulation of gene sets related to inflammatory responses, while showing an enrichment in metabolism, oxidative phosphorylation reactive oxygen species pathway gene sets. The continuous significance score (Signif) indicates the −log10(Padj) * sign(fold-change) from the GSEA. Red, upregulation; blue, downregulation. D and E, A prominent upregulation of inflammatory response related gene expression programs was noted in the TME of KRAS G12C/TP53 comutant LUADs, together with gene sets related to cell-cycle progression and E2F-driven proliferation. Quantile-quantile plots were generated to visually compare the ranks of genes in the pathway to ranks that were sampled from a discrete uniform distribution. Adjusted P values for gene set differential expression are provided for comparison of KRAS G12C/non–RAS-mutant LUAD to KRAS G12C-mutant LUAD. HM, Hallmark; KG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes, KEGG.