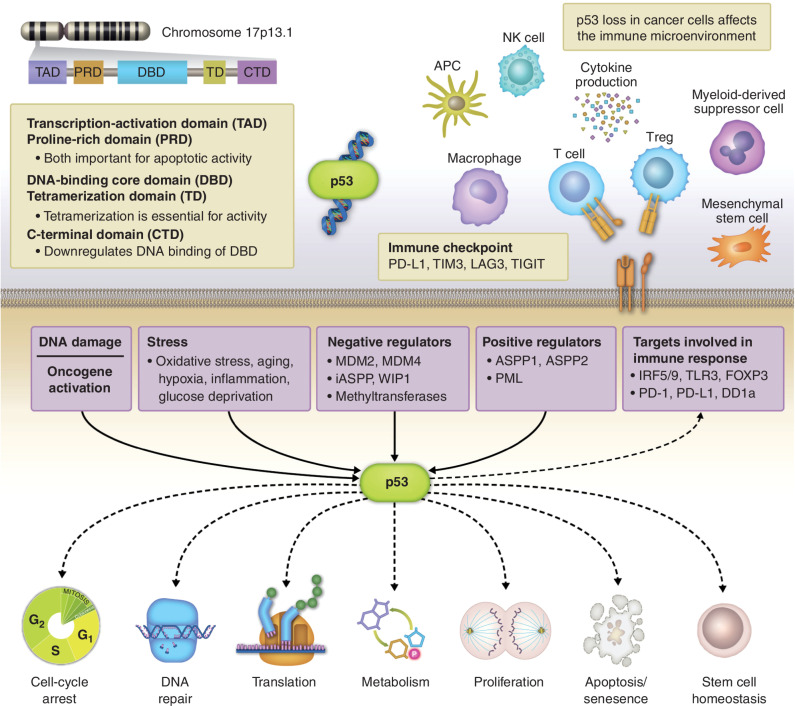
Figure 1.
Different subunits of the p53 are coded by a gene located on chromosome 17p13.1. p53 resides over a highly connected hub involving multiple signal transduction pathways, including DNA damage response, oncogene activation, cellular stress, and its positive and negative regulators. In turn, p53 regulates numerous key cellular processes including cell cycling, genomic stability, cell metabolism, differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, senescence, and others. In addition, downstream signaling through p53 influences the tumor microenvironment through a direct effect on several immunologic targets. APC, antigen-presenting cell; NK, natural killer; Treg, regulatory T cell.