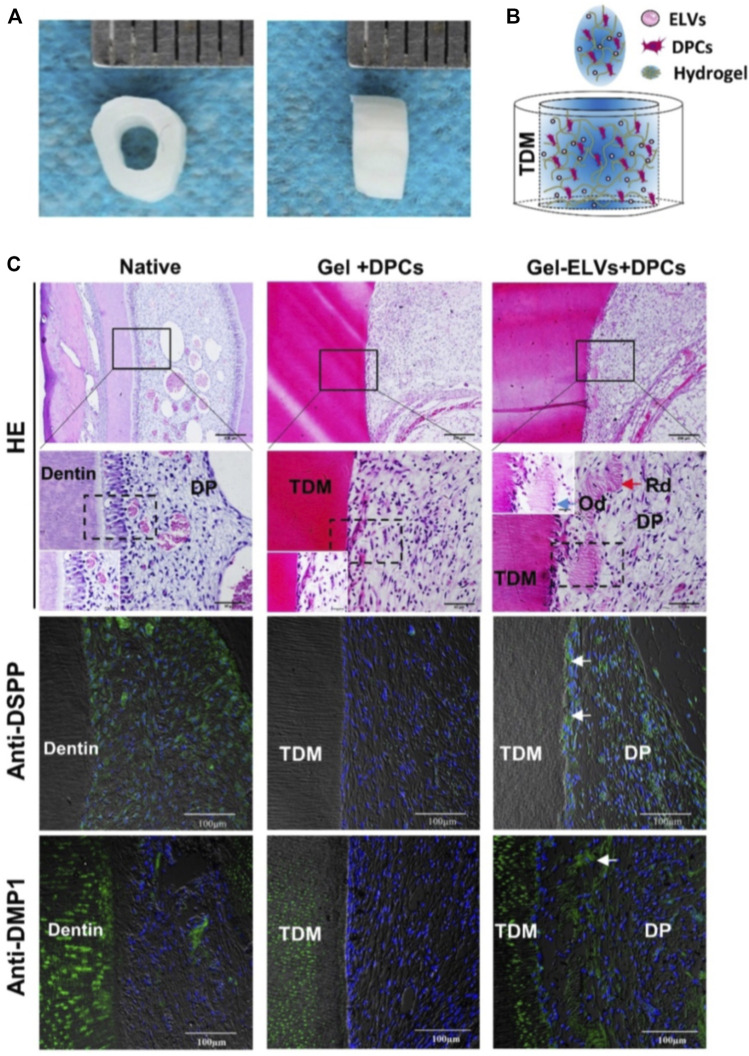
FIGURE 4.
Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath cell-derived exosome-like Vesicles (ELVs) accelerate the formation of pulp-detin complexes in vivo. (A) The treated dentin matrix (TDM) canal obtained from extracted incisors of pigs formed a tooth root slice with an internal diameter of 2 mm and a height of 3 mm. (B) Schematic of the contents of TDM. Exosome-like vesicles were resuspended in DPC cells mixed with collagen hydrogel and then injected into the tooth root slice model. (C) HE staining showing newly regenerated tooth structures (e.g., polarizing odontoblast-like cells and predentin-like tissue) at the interface between the pulp-like tissue and the dentin. Immunofluorescence analysis revealing the increased expression of odontogenic differentiation markers (DSPP and DMP1) in the ELV-treated group, with white arrows indicating positive green staining. (DPCs: Dental pulp cells; DSPP: dentin sialophosphoprotein; DMP1: dentin matrix protein 1; Rd: regenerated dentin-like tissue; Od: odontoblast-like cell; DP: dental pulp-like tissue). Scale bars are shown. (Zhang, et al., 2020a Copyright; ivyspring).