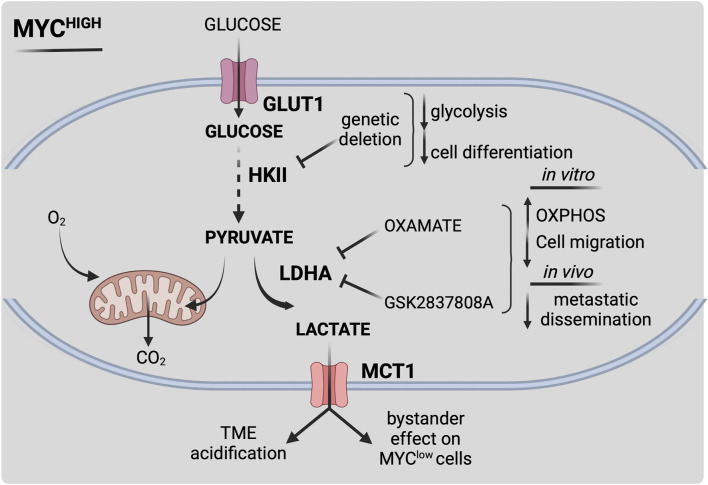
FIGURE 2.
Schematic representation of MYC-dependent metabolic reprogramming in MB. MYC overexpression or amplification (MYChigh) drives metabolic reprogramming, leading to increased survival and therapy resistance. MYC-dependent alterations lead to enhanced aerobic glycolysis (i.e., Warburg effect) by a multiple-layered regulation. Activation of MYC stimulates glucose uptake by increasing transcription levels of glucose transporter GLUT1. MYC-dependent upregulation of hexokinase 2 (HKII) and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1) fuels glucose flux within the cell. MYC highly contributes to extracellular acidification by acting on lactate synthesis and secretion through lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) and monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) expression, thus influencing MB microenvironment. Pharmacological targeting of MYC-dependent key metabolic reactions could be effective towards high-risk MYC-driven MB. Figure is created in “BioRender.com”.