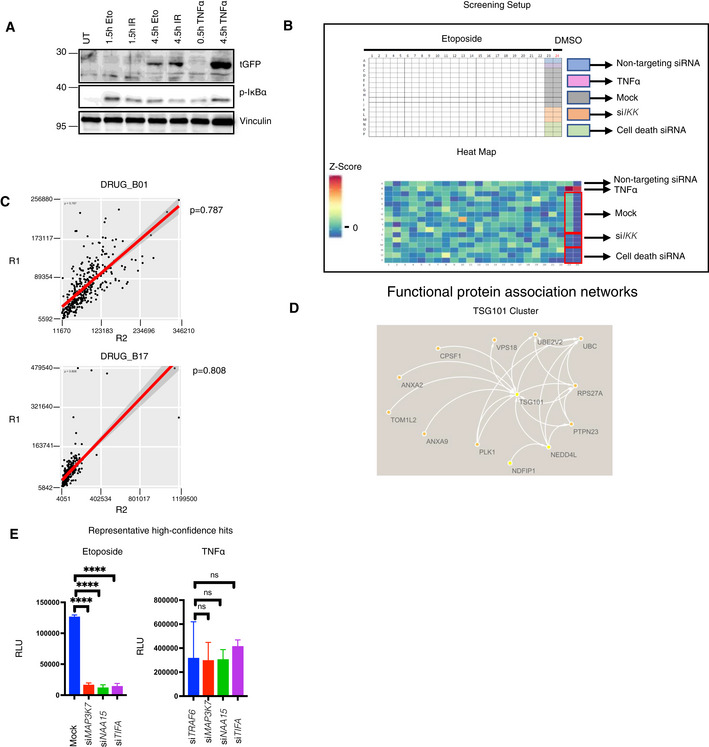
Figure EV1. Genome‐wide siRNA screening and hit selection.
-
AHEK‐Luc(tGFP) NF‐κB reporter cells were treated with the indicated conditions (50 μM etoposide, 20 Gy irradiation, or 10 ng/ml TNFα). As the NF‐κB‐driven expression and translation of turbo GFP require more time than the initial activation of the NF‐κB pathway, the treatment conditions were alternatively prolonged to 4.5 h. Whole‐cell extracts were obtained and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.
-
BDetailed layout of the genome‐wide siRNA screening, carried out using a one‐plate‐to‐one target approach. The indicated controls were added to the siRNA library. As another control, cells were treated with the vehicle DMSO (Column 24). The heatmap displays the Z‐scores of tested candidates and controls of a representative plate taken from the siRNA library screen.
-
CSpearman's rank correlation coefficient test of representative screening plate replicates demonstrated high assay reproducibility. Same screening plates and layouts were tested, and results were compared with each other (R1 vs R2).
-
DTSG101 cluster was visualized using STRING database (Szklarczyk et al, 2019). Arrows or lines between candidate hits represent protein–protein interactions observed in previous publications.
-
ERepresentative high‐confidence DNA damage‐selective hits are shown for etoposide (left panel) and TNFα (right panel) screens. The conditions were compared with an ordinary one‐way ANOVA (ns, P > 0.05; ****P < 0.0001). Results were obtained from three biologically independent experiments. Error bars represent mean ± SD.
