Fig. 2.
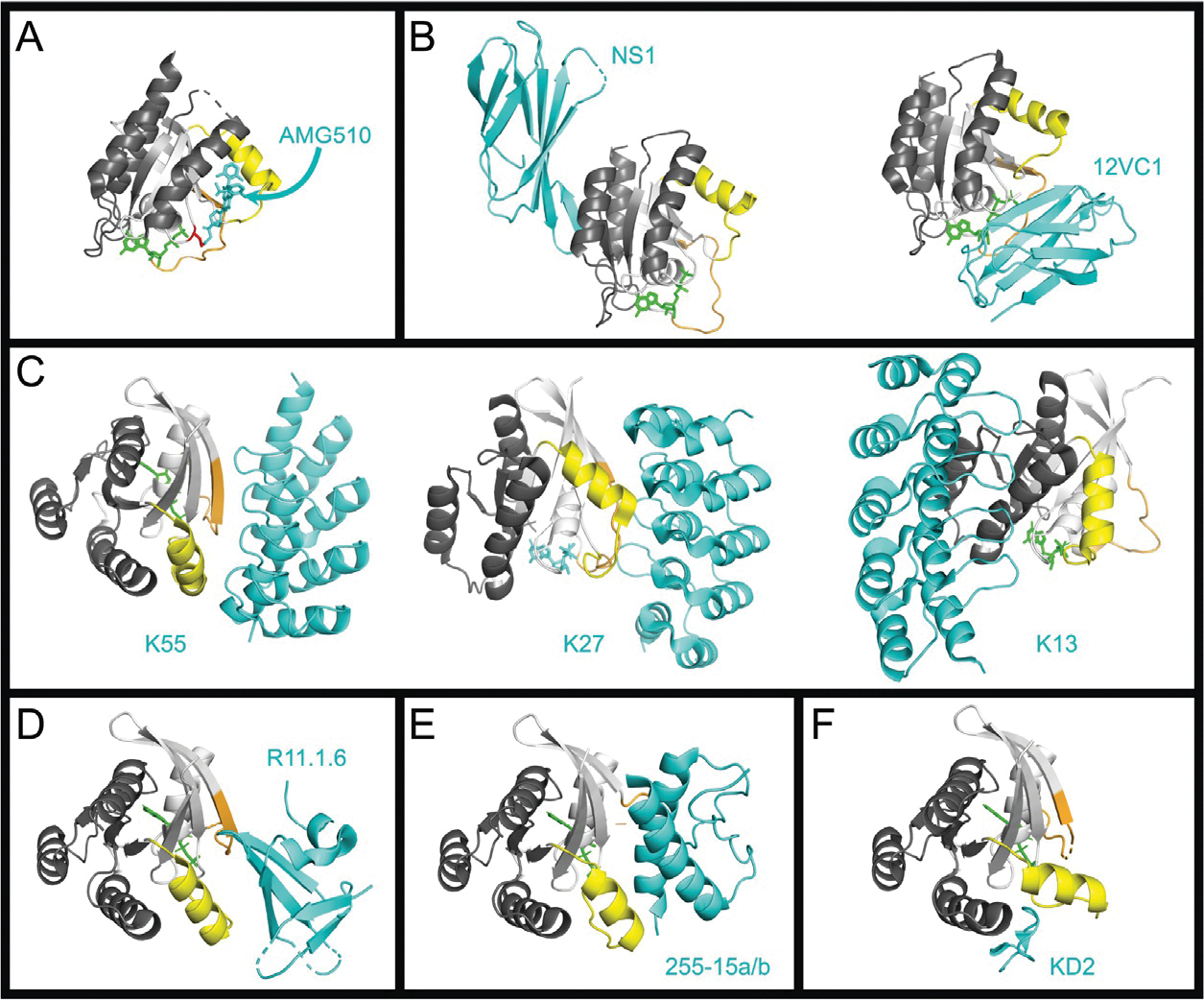
Binding interfaces of various RAS inhibitors. The crystal structures of RAS in complex with various inhibitors. For all RAS structures the effector lobe is highlighted light gray and the allosteric lobe, dark gray, Switch 1 is highlighted orange and Switch 2 highlighted yellow. All inhibitors are shown in cyan. Nucleotide is colored green. Metal ions and water molecules have been removed from structures. (A) Structure of KRASG12C bound to Sotorasib (AMG-510) (PDB 6OIM). The Cys12 is highlighted in red. (B) RAS Monobodies. HRAS:NS1, left (PDB 5E95), and HRAS(G12C):12VC1 (7L0G). (C) RAS DARPins. KRASG12V:K55, left (PDB 5MLA); KRASG12V:K27, center (PDB 5O2S); KRASG12V:K13, right (PDB 6H46). (D) Sso7d protein R11.1.6. KRASG12D:R11.1.6 (PDB RUFQ). (E) Miniprotein 225–15a/b. RASG12V:225–15a/b (PDB 5WLB). (F) KD2 cyclic peptide. KRASG12D:KD2 (PDB 6WGN).
