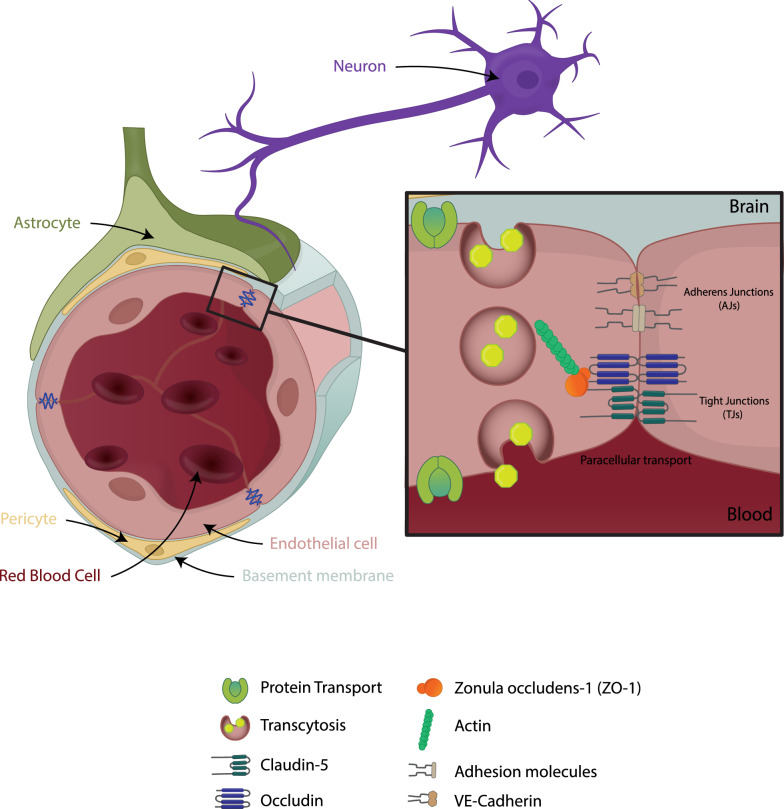
Fig. 1.
The Neurovascular Unit. In the CNS, ECs, pericytes, glia and neurons form an interdependency that allows for proper neuronal function and establishes a blood-tissue barrier that controls the passage of solutes and fluids. The BBB and BRB ECs possess unique characteristics that allow for this control, specifically the presence of TJs that seal the paracellular space and low rates of transcytosis. TJs are formed by long strands of transmembrane proteins including: claudins, occludin and tricellulin that are connected to the actin cytoskeleton by scaffold ZO proteins