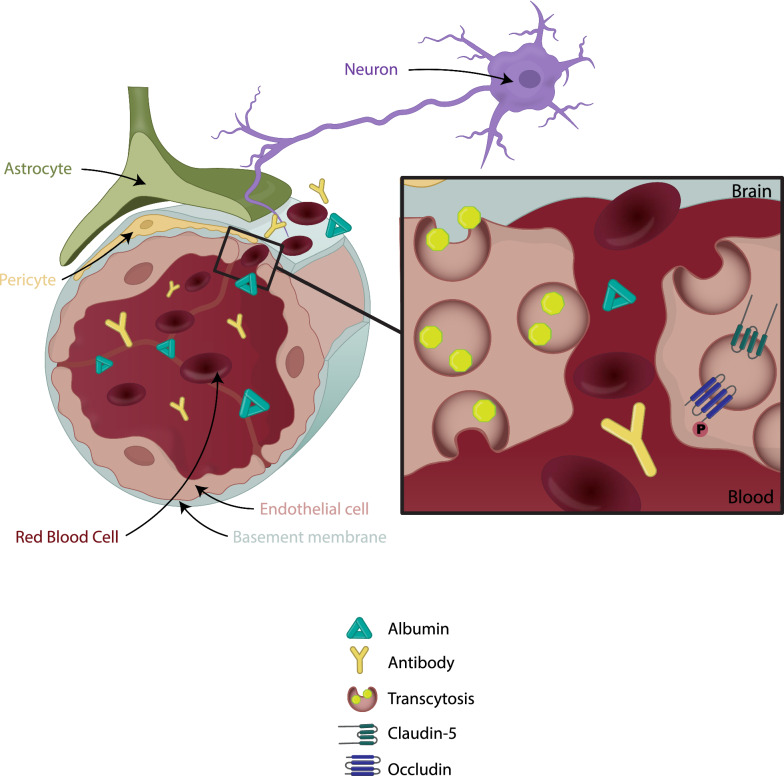
Fig. 3.
Neurovascular unit breakdown. In several disease states, such as stroke or diabetic retinopathy, a number of factors contribute to BBB breakdown and both paracellular and transcellular transport are increased. Loss of pericytes and gliosis further exacerbate the increase in permeability leading to infiltration of harmful substances to neurons and causing neuronal dysfunction. The process of barrier loss and neural degeneration is hypothesized to lead to a feed-forward pathology extending the disease process. Methods that target barrier breakdown may halt this process