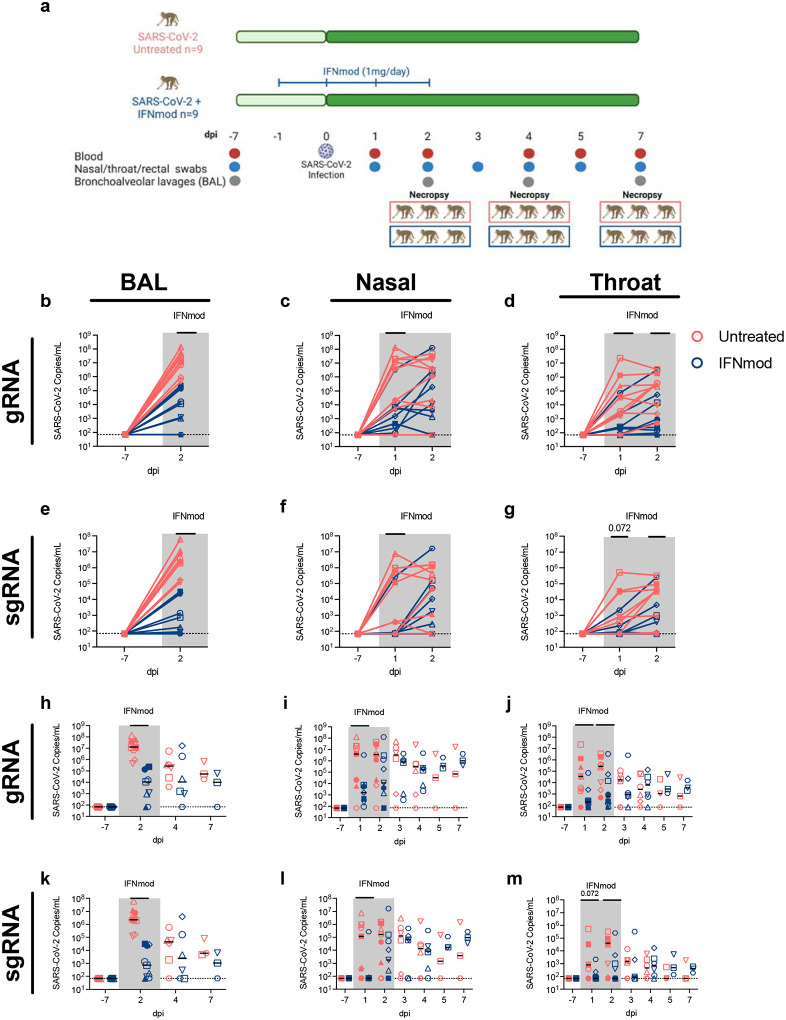
Fig. 1. IFNmod administration results in significant reduction in viral loads of SARS-CoV-2 infected RMs.
(a) Study Design; 18 RMs were infected intranasally and intratracheally with SARS-CoV-2. 1 day prior to infection (−1dpi), 9 RMs started a 4-dose regimen of IFNmod (1mg/day) that continued up until 2dpi while the other 9 RMs remained untreated. RMs were sacrificed at 2, 4, or 7 dpi. Levels of SARS-CoV-2 gRNA N (b-d) and sgRNA E (e-g) in BAL, nasopharyngeal swabs, and throat swabs during IFNmod treatment. Levels of SARS-CoV-2 gRNA N (h-j) and sgRNA E (k-m) in BAL, nasopharyngeal swabs, and throat swabs longitudinally throughout the entire duration of the study. Untreated animals are depicted in red and IFNmod-treated animals are depicted in blue. Black lines in h-m represent median viral loads for each treatment group at each timepoint. Gray-shaded boxes indicate that timepoint occurred during IFNmod treatment. Statistical analyses were performed using non-parametric Mann-Whitney tests. * p-value < 0.05, ** p-value < 0.01.