Figure 3.
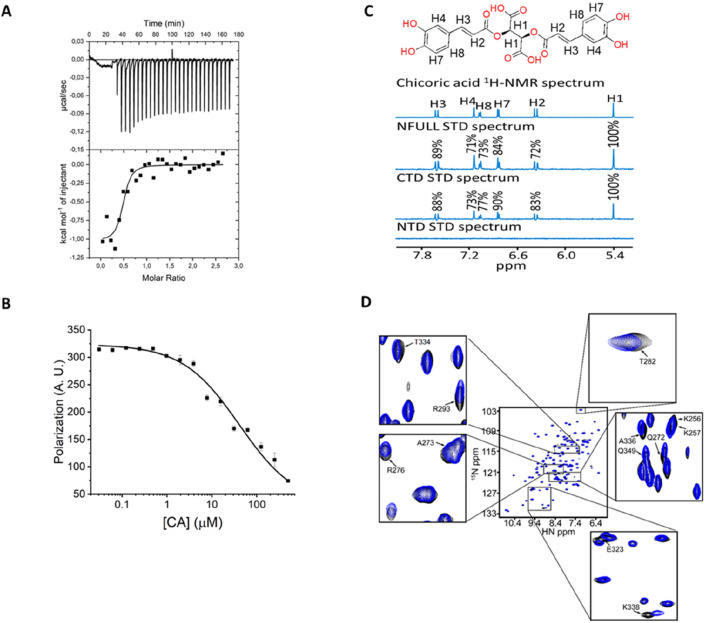
Chicoric acid (CA) is a nanomolar N-protein affinity ligand that binds the CTD and promotes dissociation of the N protein-RNA1 complex. (A) ITC assay showing the thermodynamic parameters of interaction between the N protein and CA. The free N protein (20 µM) was titrated against CA (250 µM). The data were fitted to the One Set of Site model, resulting in the following thermodynamic parameters: association constant (KA) = 2.27E6 1.3E6 M-1 (KD = 0.25 7.9 E-9 µM); binding enthalpy change (ΔH) = − 953.2 104.4 cal/mol and binding entropy change (ΔS) = 27.0 1.0 cal/mol/deg. The isotherm is representative of three replicates and the values reported are average and standard deviation of the three independent experiments. (B) Dissociation curve showing that CA promotes the dissociation of previously formed N protein-RNA1 complex with a KD value of 41.1 ± 11.7 µM. (C) One-dimension 1H-STD NMR spectra of CA in the presence of free N protein (full-length), CTD or NTD. The relative degree of saturation of each hydrogen atom of CA is mapped onto each spectrum and normalized by hydrogen H1. (D) 1H-15 N-HSQC spectra of free 15 N-CTD in the absence (black signals) or presence (blue signals) of CA in a 1:1 protein:CA ratio. Assigned peaks were based on the BMRB entry 50,518. Highlighted peaks correspond to signals that changed by more than 0.02 ppm using the deviation equation Δδ(15 N + 1H) = [(Δδ15N/10)2 + (Δδ1H)2]1/2.