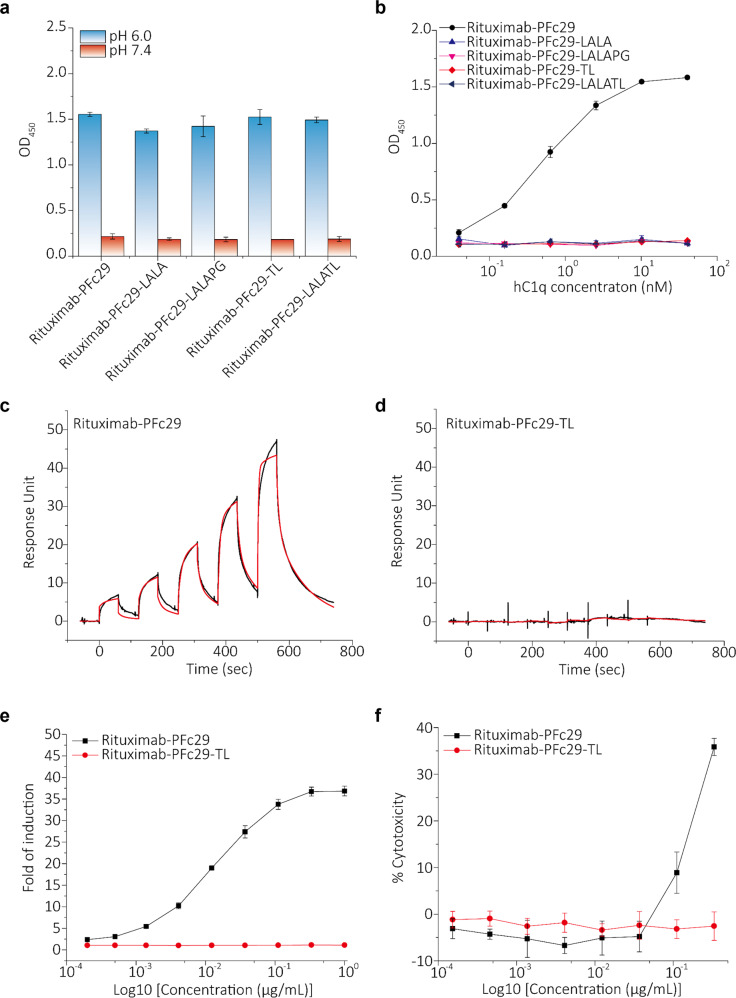
Fig. 5. Analysis of the binding of Fc ligands (hFcRn, C1q, and hFcγRIIIa) and effector functions (ADCC and CDC) when the two mutations of PFc29 were combined with effector function-silencing mutations (LALA, LALAPG, or TL).
a ELISA binding signals (OD450) upon binding rituximab-PFc29, rituximab-PFc29-LALA, rituximab-PFc29-LALAPG, rituximab-PFc29-TL, and rituximab-PFc29-LALATL to hFcRn at two pH conditions (pH 6.0 and pH 7.4) are represented as a bar graph. Errors bars indicate the standard deviations calculated from duplicate samples. b ELISA binding signals (OD450) upon binding rituximab-PFc29, rituximab-PFc29-LALA, rituximab-PFc29-LALAPG, rituximab-PFc29-TL, and rituximab-PFc29-LALATL to C1q are represented as a graph. c, d SPR sensorgrams showing the binding of rituximab-Fc variants to hFcγRIIIa. Interactions between hFcγRIIIa and rituximab-PFc29 c and rituximab-PFc29-TL d were analyzed using an SPR instrument. e ADCC activities of rituximab-PFc29-TL and rituximab-PFc29. Raji cells and engineered Jurkat cells expressing FcγRIIIa-158V were used as target cells and effector cells, respectively. f CDC activities of rituximab-PFc29-TL and rituximab-PFc29. Cytotoxicity was measured using Raji cells and normal human complements.