Figure 4.
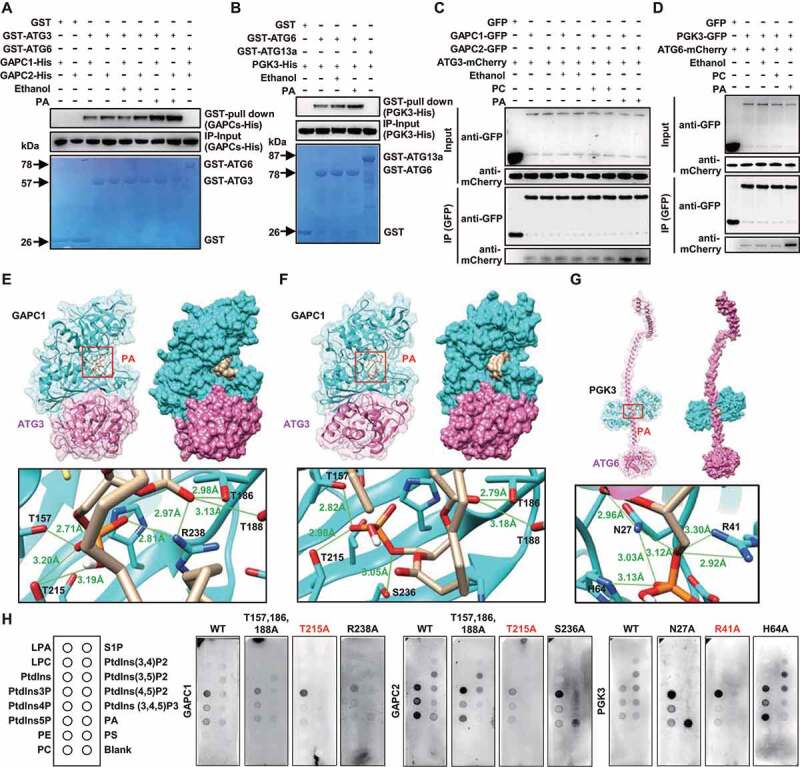
PA binds to GAPCs or PGK3 and promotes the interaction of GAPCs-ATG3 or PGK3-ATG6 in vivo and in vitro. (A and B) GAPCs-His (A) or PGK3-His (B) was precipitated by GST-ATG3 (A, GST-ATG6 was used as negative control) or GST-ATG6 (B, GST-ATG13a was used as negative control) using agarose beads in the absence or presence of PA (10 μM). The pellet fraction was eluted and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-His antibodies (upper panel). Input of His-tagged proteins (middle panel) and equal aliquots of glutathione beads loaded with GST-ATG3 or GST-ATG6 or GST (separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue, bottom panel) were shown. (C and D) PA promotes the formation of GAPCs-ATG3 (C) or PGK3-ATG6 (D) complexes in vivo. Cell lysate from Arabidopsis seedlings expressing GAPCs-GFP and ATG3-mCherry or PGK3-GFP and ATG6-mCherry was subjected to a GFP trap assay. Resultant immunoprecipitation (IP) and cell lysate were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-GFP or anti-mCherry antibodies. (E-G) Structural diagram of the PA-GAPCs-ATG3 (E, F) or PA-PGK3-ATG6 (G) complex based on the flexible docking model. Proteins are shown in the cartoon and surface model, with GAPCs or PGK3 colored in cyan, ATG3 or ATG6 colored in pink and 18:1 PA colored in yellow. In the zoom graph, the amino acids of GAPCs or PGK3 protein that could establish hydrogen bonds with PA are predicted based on the docking model. Green font and lines indicate the hydrogen bonds and distances. (H) Lipid-protein blot overlay assays of the PA binding capacity of GAPCs and PGK3 (WT and variants containing various amino acid mutation). Recombinant expressed GAPCs, PGK3, and variants (fused with His-tag) were incubated with PIP strips and detected using anti-His antibodies. LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphocholine; PtdIns, phosphatidylinositol; PtdIns3P, PtdIns-3-phosphate; PtdIns4P, PtdIns-4-phosphate; PtdIns5P, PtdIns-5-phosphate; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; PtdIns(3,4)P2, PtdIns-3,4-bisphosphate; PtdIns(3,5)P2, PtdIns-3,5-bisphosphate; PtdIns(4,5)P2, PtdIns-4,5-bisphosphate; PtdIns(3,4,5)P3, PtdIns-3,4,5-trisphosphate; PA, phosphatidic acid; PS, phosphatidylserine.
