Figure 5.
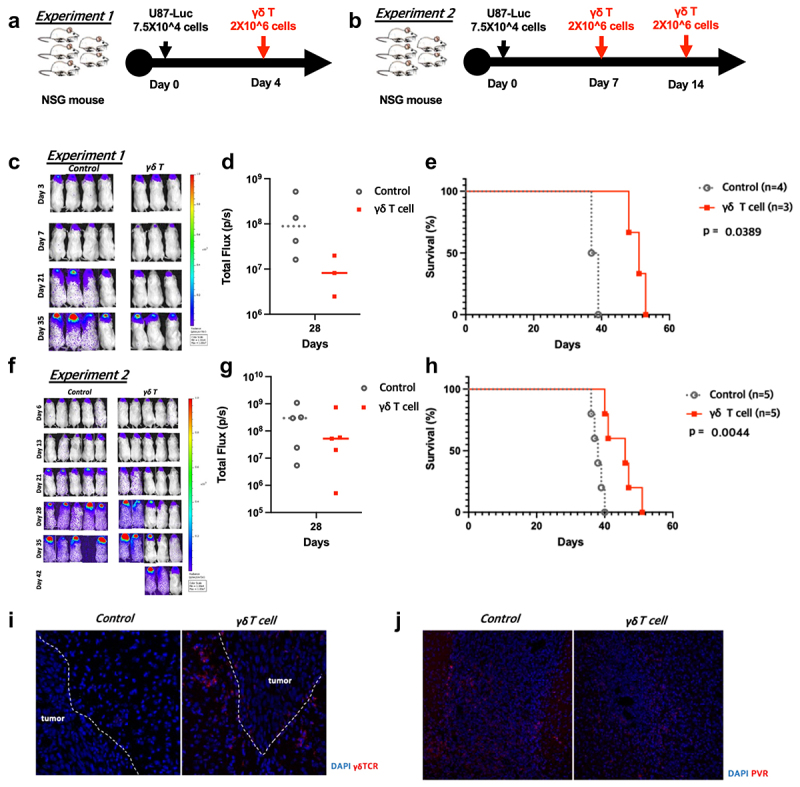
In vivo anti-tumor effects of human γδ T cells in an intracranial U87 NSG mouse model. (a,b) Intracranial injections of 5 × 104 U87 cells were done on day 0, and the mice were randomized into two groups on the treatment day. We performed intratumoral injections of PBS (control group) or 2 × 106 human γδ T cells (γδ T cell group) following two schedules (experiment 1: on day 4, experiment 2: on days 7 and 14). (c,f) Tumor growth was weekly monitored by IVIS and the average radiance per mouse were analyzed, following treatments. (d,g) Total photons were calculated by IVIS Lumina XRMS. (e,h) A Kaplan-Meier survival curve of intracranial glioblastoma–bearing mice intratumorally treated with PBS (control) or human γδ T cells (γδ T cell) is presented. (i) Infiltrating γδ T cells within tumors from each group are shown from day 10 after tumor implantation. (j) PVR expression in each group on day 10 after tumor implantation.
