Figure 5.
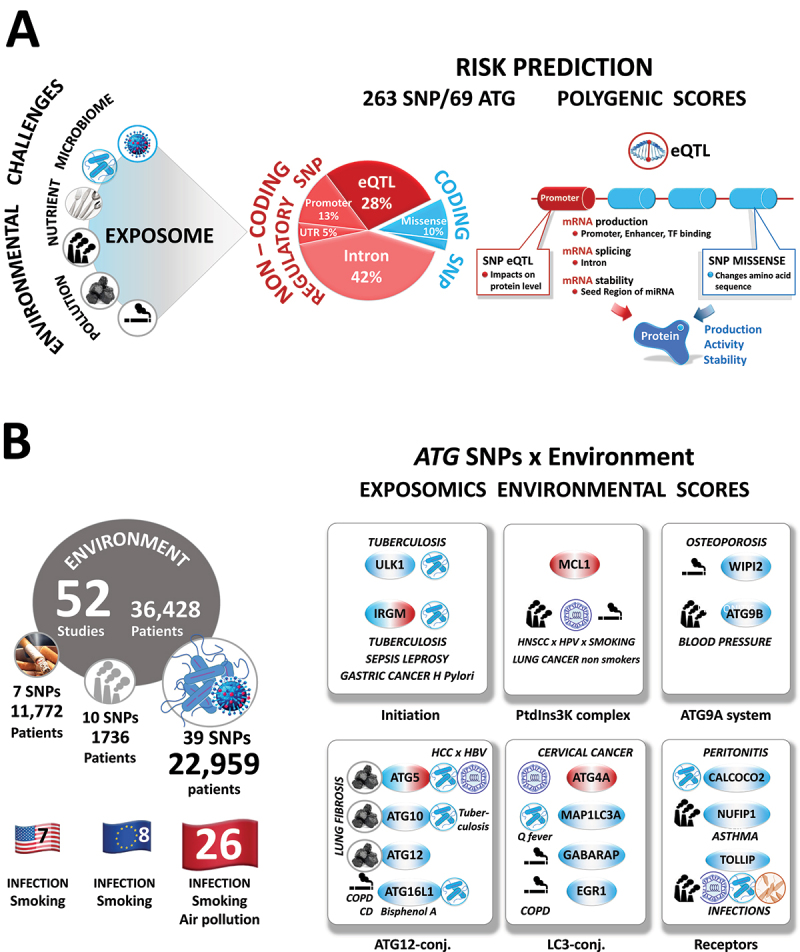
Biomarkers of exposure and, ultimately, of risk assessment and clinical outcome. (A) Right. Distribution (in percentage, left) and predicted functional consequences (right) of 219 coding and non-coding regulatory ATG SNPs. Left, Number of studies, totaling the number of patients, ATG genes, and SNP per Europe, United States, and Asia. Note that whereas 70 to 90% of the risk of developing a disease is due to the environment, only 13% of studies on autophagy gene SNPs have included the environment as a trigger or exacerbating factor. Likewise, air pollution is the fourth most prevalent deadly risk factor worldwide and, so far, most of the studies focused on infection. TF, transcription factor. Related to: (B) The concept of the exposome and atlas of the ‘autophagy gene × environmental’ interactions in the susceptibility of complex human diseases. Because of the long latency period, exposure to a causal agent/mixture typically occurs years to decades before disease diagnosis. The exposome is a unique marker that characterizes the totality of trace chemicals resulting from different routes (internal and external) and times of exposure over the lifetime of an individual.
