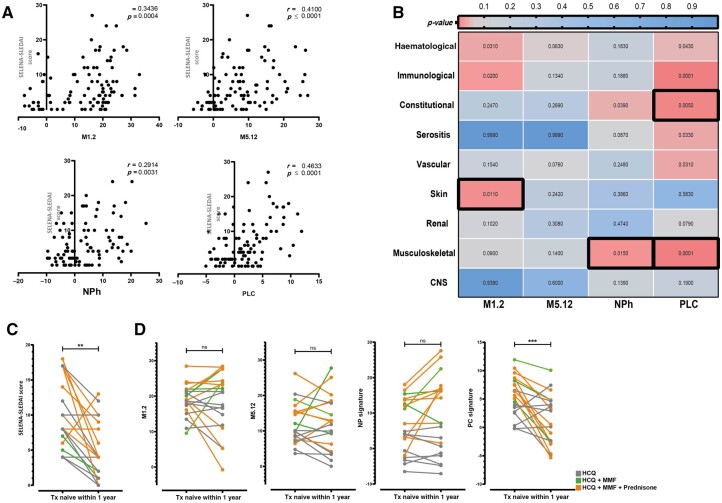
Fig. 2.
Gene signatures are associated with disease activity
(A) Correlation between the SELENA-SLEDAI and gene signature scores. (B) Heatmap indicating the correlation between a high signature and a specific disease domain derived from the SELENA-SLEDAI. Numbers indicate the P-value based on univariate analysis. Black outlined boxes indicate domains that were significant in the multivariate model. (C) Longitudinal SELENA-SLEDAI and (D) gene signature scores from 20 Txnaive cSLE patients at the first and second time points (median time between two samples = 62.5 days). The Mann–Whitney U-test was used to compare two groups; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. For correlations, Spearman’s rho was used. Fisher’s exact test was used to compare categorical data. cSLE: childhood-onset SLE; NPh: neutrophil signature;ns: not significant; PLC: plasma cell signature; SELENA: Safety of Estrogen in Lupus National Assessment; Txnaive: treatment naïve.