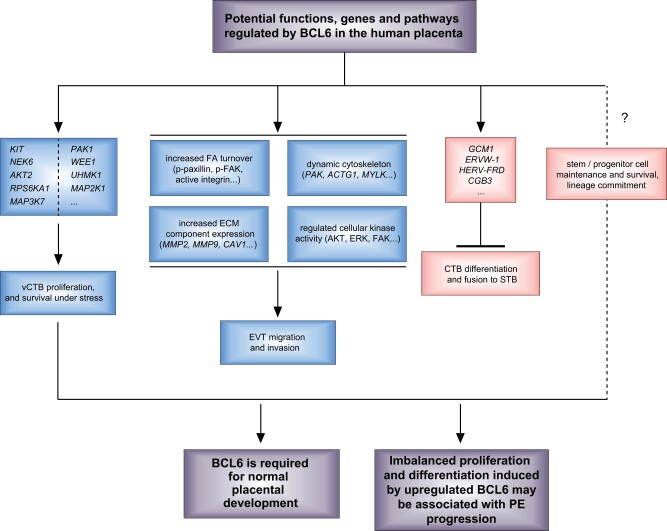
Figure 4.
Potential functions of BCL6 in the human placenta. BCL6 promotes proliferation and survival of vCTBs, facilitates migration and invasion of EVTs, and inhibits differentiation and fusion of vCTBs into the STB. BCL6 may also affect trophoblast stem/progenitor cell survival and differentiation. Upregulated BCL6 may cause imbalanced proliferation and differentiation, contributing to the pathogenesis of PE. ACTG, actin gamma; AKT2, AKT serine/threonine kinase 2; CAV1, caveolin 1; CGB3, chorionic gonadotropin subunit beta 3; ECM, extracellular matrix; ERVW-1, endogenous retrovirus group W member 1, syncytin1; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GCM1, glial cells missing transcription factor 1; HERV-FRD, human endogenous retrovirus group FRD, syncytin 2; KIT, receptor tyrosine kinase; MAP2K1, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1; MAP3K7, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase 1; MMP, matrix metallopeptidase; MYLK, myosin light chain kinase; NEK6, NIMA-related kinase 6; PAK1, p21-activated kinase 1; RPS6KA1, ribosomal protein S6 kinase A1; UHMK1, U2 small nuclear RNA auxiliary factor 2 homology motif kinase 1; WEE1, G2 checkpoint kinase.