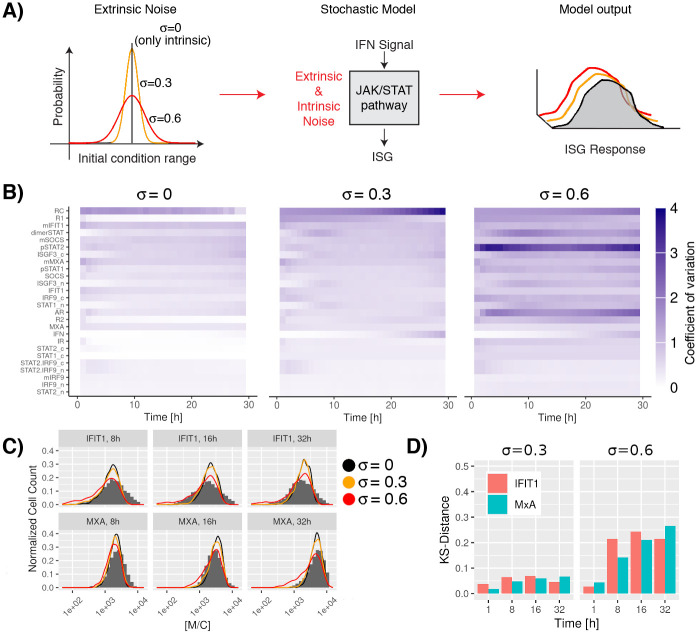
Fig 5. Effect of extrinsic noise in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway.
A: Extrinsic noise in the system was introduced by considering the effect of variability in the initial copy number of the proteins in the pathway. Initial conditions were generated by random sampling using a normal distribution with values for μ given in Table 1 and one of three values of σ: 0, 0.3, 0.6. B: Variability in the elements of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway over time. The effects of extrinsic noise in the system were calculated by the coefficient of variation (cv = σS/(μS + 0.1), where the subindex s represents the species in the pathway). In the plot the colorbar varies between 0 (white color) and larger than 4 (blue color), dark colors represent high variability in the dynamics of the studied species. Species were ordered based on the average coefficient of variation over all time points for systems with an extrinsic noise of σ = 0.3. The overall system dynamics under the influence of extrinsic noise can also be observed in Figs J to L in S1 Text. C: Stochastic simulations of different time points after IFN stimulation using a distribution of values as initial conditions. The results show a transient perturbation in the MxA and IFIT1 expression when extrinsic fluctuations are considered. As reference, experimental data for a system without extrinsic noise (σ = 0.0) are given (gray histograms). D: Distributions at multiple time points considering different strengths of extrinsic noise vs a system with only intrinsic noise are compared using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov distance.