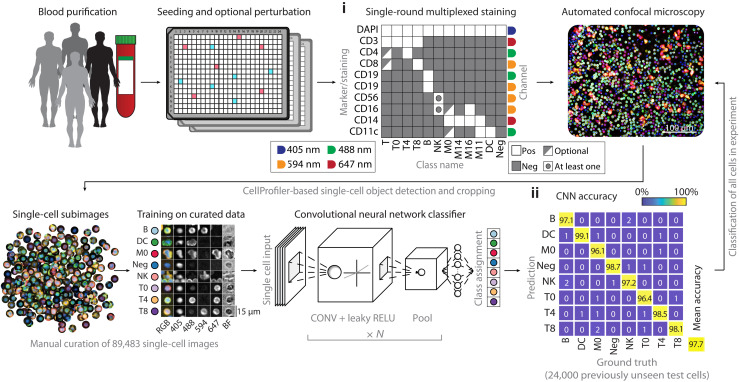
Fig. 1. Deep learning–enabled multiplexed immunofluorescence and microscopy of human immune cells.
Workflow for the single-round multiplexed immunofluorescence, image-based screening, and associated deep learning–based classification of human PBMCs. PBMCs of healthy human donors are seeded in 384-well plates, optionally containing drugs or immune stimuli. Cells are fixed and stained with a comprehensive antibody panel (i) and imaged by automated confocal microscopy. A CNN is trained on 89,483 manually curated subimages to distinguish eight different immune cell classes and subsequently classifies all cells in the experiment. The curated test set contains 100 cells per class per donor per staining condition. (ii) Confusion matrix of CNN performance across all 24,000 cells that the CNN did not see before. CONV, convolution; RELU, rectified linear unit.