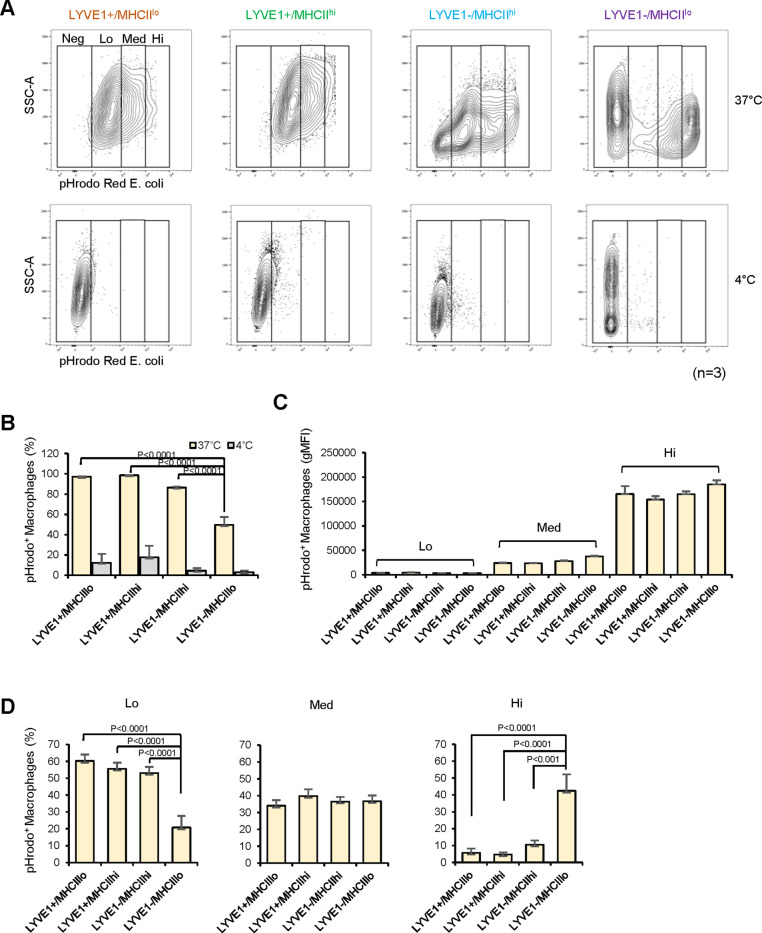
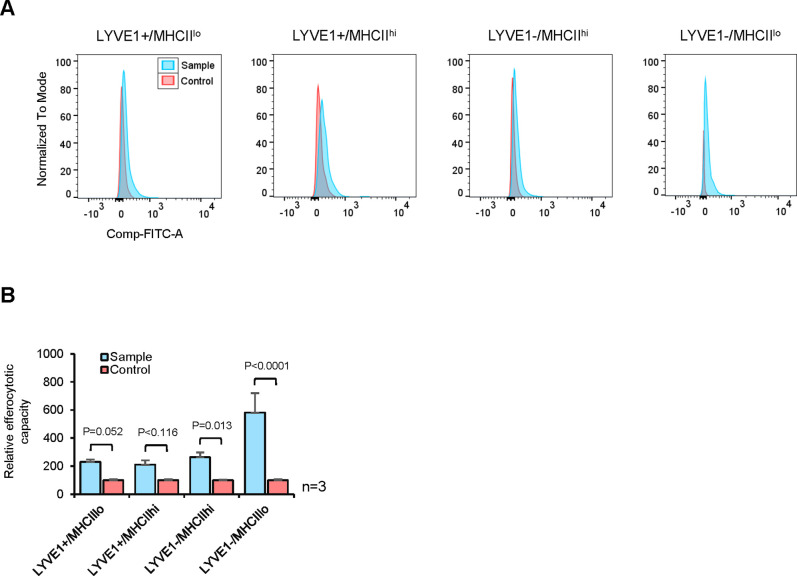
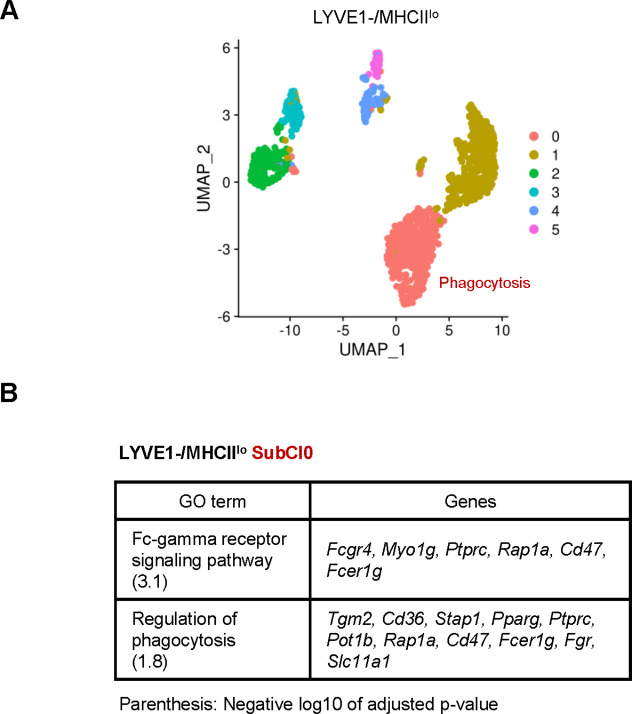
Figure 5. Analysis of the phagocytic capacities of each macrophage subgroup.
(A) Phagocytic activity was measured for mouse skeletal muscle (SKM) macrophages at 4°C (control, low phagocytosis) and 37°C (active phagocytosis, right boxes). Phagocytic capacity was divided into groups that were negative (Neg; intensity <103), low (Lo; 103–104), medium (Med; 104–105), and high (Hi; >105), depending on signal intensities. Gating was established using fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls for each experiment. (B) Quantification of the macrophages showing active phagocytosis (Lo + Med + Hi) in the four subgroups. (C) Signal intensities of macrophages in each capacity group (Lo, Med, and Hi). (D) Quantification of number of active phagocytic macrophages in each subgroup of the three intensity groups. Data are representative of three independent experiments.