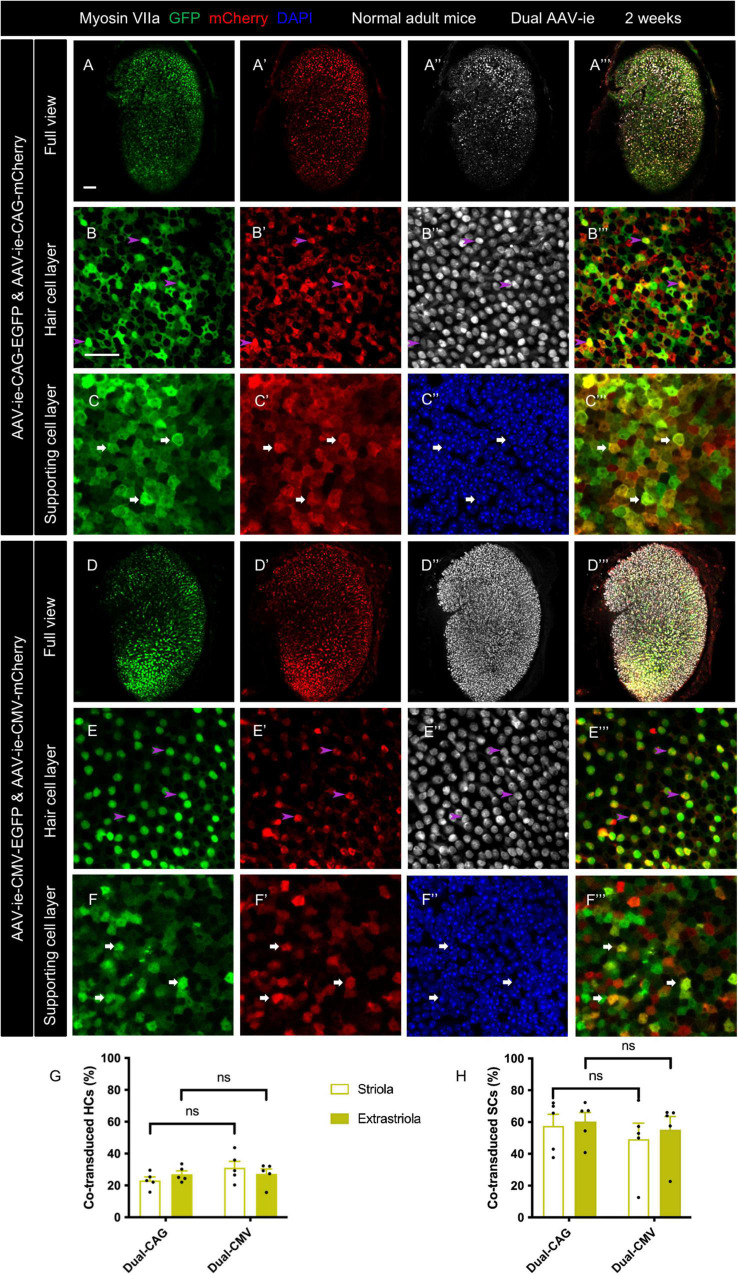
FIGURE 1.
Co-transduction of dual-AAV-ie vectors in the normal adult mouse utricle. Dual AAV-ie-CAG vectors (AAV-ie-CAG-EGFP and AAV-ie-CAG-mCherry) or dual AAV-ie-CMV vectors (AAV-ie-CMV-EGFP and AAV-ie-CMV-mCherry) were inoculated into the inner ear of adult mice. Utricles were harvested 2 weeks after the surgery. (A–C”’) Low- (A–A”’) and high- (B–C”’) magnification images show extensive co-expression of GFP and mCherry in both HCs (arrowheads in B–B”’; representative images of the extrastriolar region) and SCs (arrows in C–C”’; representative images of the striolar region) after transduction by dual AAV-ie-CAG vectors. (D–F”’) Abundant HCs (arrowheads in E–E”’; representative images of the extrastriolar region) and SCs (arrows in F–F”’; representative images of the extrastriolar region) express both GFP and mCherry after transduction by dual-AAV-ie-CMV vectors. Scale bars, 50 μm in A for (A–A”’) and (D–D”’); 20 μm in B for the remaining images. (G,H) Quantitative analysis showing that dual-AAV-ie-CAG and dual-AAV-ie-CMV vectors achieve comparable co-transduction rates in HCs (G) and SCs (H). Data are mean ± SEM. P-values were calculated by Student’s t-test. “ns”, not significant.