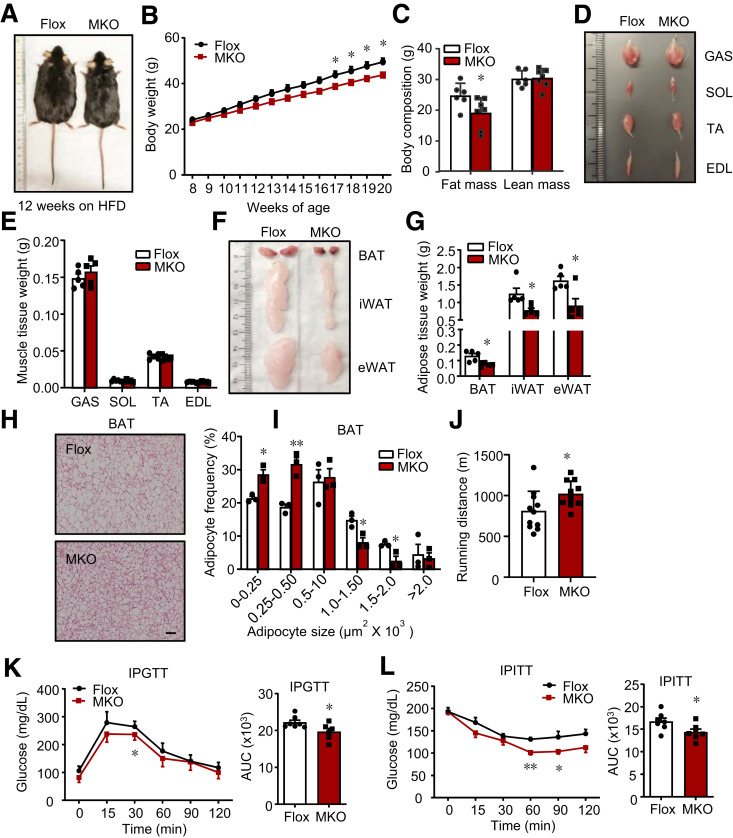
Figure 3.
Mice with IRF4 ablation in skeletal muscle are resistant to HFD-induced obesity. A: The morphology of male MKO and Flox mice on 12-week HFD. B: The body weight of male MKO and Flox mice on HFD (n = 8–10) (*P < 0.05). C: The body composition of male mice from A (n = 6–7) (*P < 0.05). D: The morphology of GAS, soleus (SOL), tibialis anterior (TA), and extensor digitorum longus (EDL) in male MKO and Flox mice on 12-week HFD. E: The weight of GAS, soleus, tibialis anterior, and extensor digitorum longus in male MKO and Flox mice on 12-week HFD (n = 5). F: The morphology of BAT, iWAT, and eWAT in male MKO and Flox mice on 12-week HFD. G: The weight of BAT, iWAT, and eWAT from mice on 12-week HFD (n = 5) (*P < 0.05). H: Hematoxylin-eosin staining and adipocyte number of BAT in male MKO and Flox mice on 12-week HFD (scale bars, 50 μm). I: The adipocyte frequency of different adipocyte size of BAT from H (n = 3) (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). J: The running distance of male MKO and Flox mice (n = 10–11) (*P < 0.05). K and L: GTT and ITT in male MKO and Flox mice (n = 6–7) (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). All results are expressed as means ± SEM. IPGTT, intraperitoneal GTT; IPTT, intraperitoneal ITT.