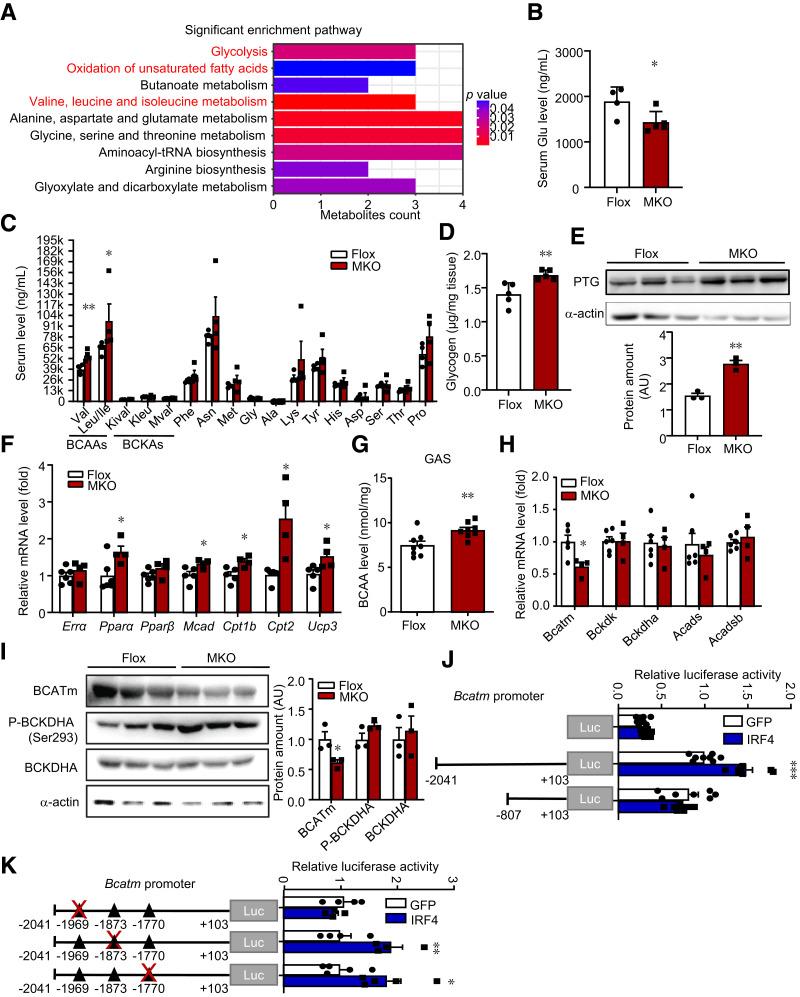
Figure 5.
IRF4 in skeletal muscle reprograms metabolome and transcriptionally regulates BCATm. A: Pathway analysis of 40 changed metabolites from targeted metabolomics data. B: Serum glucose (Glu) levels in MKO and Flox mice on HFD (n = 4–5) (*P < 0.05). C: Serum amino acids levels in MKO and Flox mice on HFD (n = 4) (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). D: The glycogen level of GAS in male MKO and Flox mice (n = 5) (**P < 0.01). E: Western blot analysis of the expression of PTG in skeletal muscle of MKO and Flox mice. Protein amount was quantified with ImageJ (n = 3) (**P < 0.01). F: Quantitative PCR analysis of FAO genes in GAS from MKO and Flox mice (n = 4–6) (*P < 0.05). G: BCAA level in GAS of MKO and Flox mice (n = 6–8) (***P < 0.001). H: Quantitative PCR analysis of gene expression relative to BCAA catabolism in GAS of male MKO and Flox mice on HFD (n = 8) (*P < 0.05). I: Western blot analysis of BCAA catabolism in GAS of MKO and Flox mice. Protein amount was quantified with ImageJ (n = 3) (*P < 0.05). P-, phosphorylated. J: Dual luciferase assays of Bcatm promoter. Luciferase activity was corrected for Renilla luciferase activity and normalized to GFP group (n = 7–8) (***P < 0.001). K: The mutant Bcatm promoter fused to a luciferase reporter gene was cotransfected into HEK293T cells together with pCDH-GFP or pCDH-IRF4. Luciferase activity was corrected for Renilla luciferase activity and normalized to GFP group (n = 4–5) (*P < 0.05). All results are expressed as means ± SEM. AU, arbitrary units; Kival, 2-ketoisovaleric acid; Kleu, ketoleucine; Mval, 2-oxo-3-methylvaleric acid.