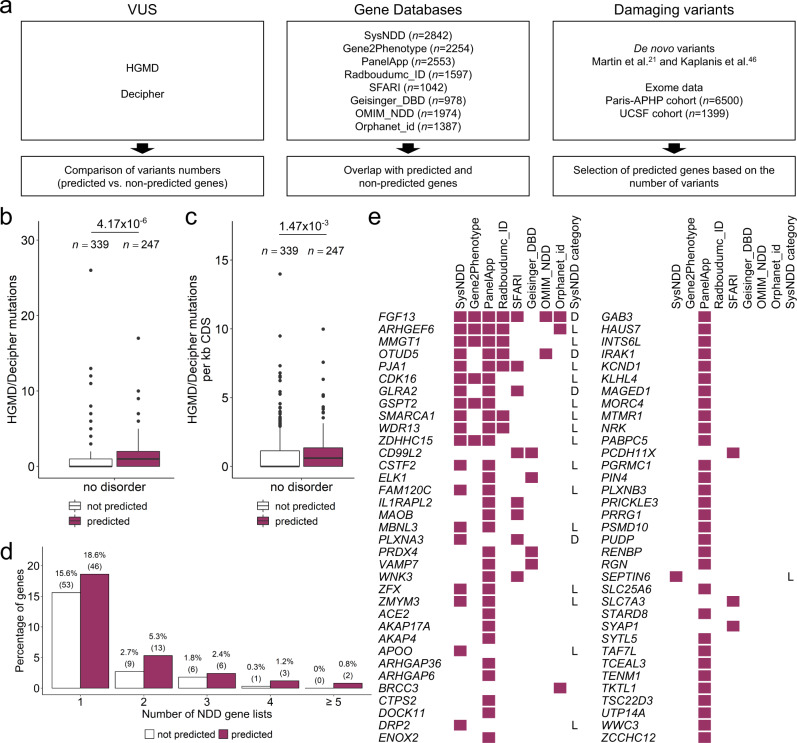
Fig. 6. External supporting evidence for the predicted disorder-associated genes.
a Sources of data reinforcing predicted genes as putative disorder-associated included variant or expert curated NDD gene databases, literature and exome data examination from two additional cohorts of patients with developmental disorders. Known point mutations in no-disorder genes. Boxplot showing the number of known mutations reported in HGMD and DECIPHER (b) or their value normalized by coding-sequence (CDS) length (c) according to their predicted status. Box plot elements are defined as follows: center line: median; box limits: upper and lower quartiles; whiskers: 1.5× interquartile range; points: outliers. d Percentage of each class of no-disorder genes present in the expert curated NDD gene databases. Number of genes are shown in brackets. b–d White, non-predicted no-disorder genes; purple, predicted no-disorder genes. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. e ML-predicted genes present in expert curated NDD gene databases. Genes in SysNDD are classified as D (definite NDD gene) or L (limited evidence as NDD gene). Data underlying this scheme can be found in Supplementary Data 8.