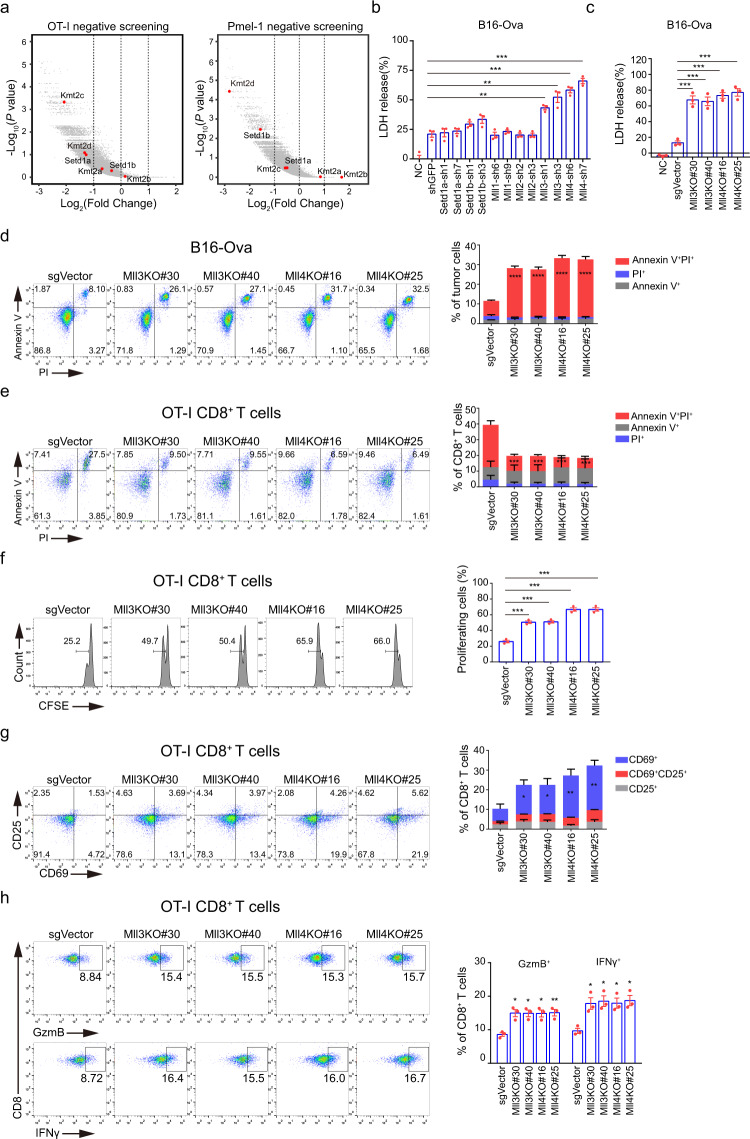
Fig. 1. Loss of Mll3 and Mll4 in tumor cells stimulates activation and cytotoxicity of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells in vitro.
a Volcano plots showing in vitro CRISPR/Cas9 screening of tumor-cell-intrinsic factors that regulates cytotoxicity of OT-I and Pmel-1 CD8+ T cells. Genes were plotted based on mean log2 fold change of gRNA counts compared to control selection. H3K4 methyltransferases of the COMPASS family were highlighted in red. Datasets for OT-I and Pmel-1 screening were from Pan et al.43 and reanalyzed in this study. b B16-Ova tumor cells depleted for the indicated H3K4 methyltransferase were incubated with OT-I CD8+ T cells at an effector to target (E/T) ratio of 10:1 for 24 h. OT-I T-cell-mediated killing was determined by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release-based cell death analyses. c, d Two independent Mll3 or Mll4 knockout (KO) B16-Ova clonal cells were co-cultured with OT-I CD8+ T cells for 24 h and tumor-cell death was analyzed by LDH release (c) and Annexin V/PI staining (d). e, f The experiment was conducted as in (b) followed by cell death (e) and proliferation (f) analyses of OT-I CD8+ T cells by flow cytometry. g, h The experiment was performed as in (b) followed by activation (g) and cytotoxicity (h) analyses of OT-I CD8+ T cells by flow cytometry. Quantification in (b–h) was shown as mean ± SEM from three biological replicates. Statistical significance was determined by MaGeCK (Model-based Analysis of Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 Knockout) (a) and two-tailed unpaired t test (b–h). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.