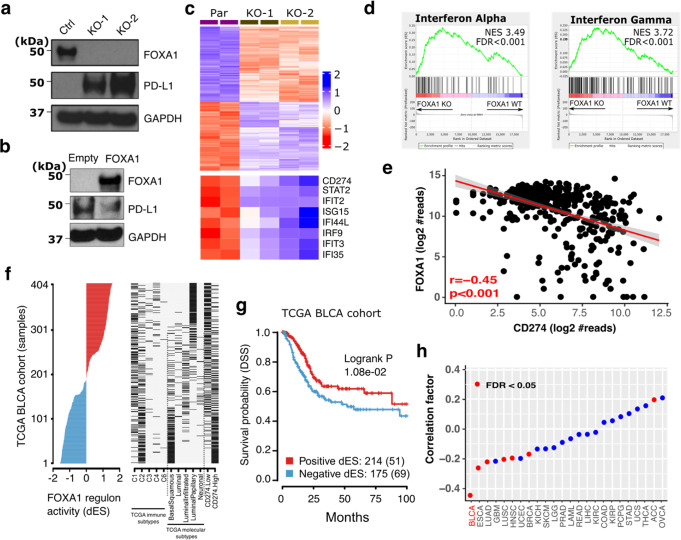
Fig. 5. Genetic ablation of FOXA1 in bladder cancer cells results in increased expression of PD-L1 and interferon sensitive genes (ISGs).
a CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing was used to generate isogenic UM-UC-1 bladder cancer cells with loss of FOXA1 expression. Immunoblot analysis showing that loss of FOXA1 expression was associated with increased PD-L1 expression. This analysis was performed in triplicate. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. b UM-UC-3 cells were transfected with FOXA1 or with empty vector. Immunoblot analysis was then performed to quantitate expression of FOXA1, PD-L1, and GAPDH as a loading control. This analysis was performed in triplicate. c Differential gene expression (FDR q < 0.05) in parental and FOXA1-KO UM-UC-1 bladder cancer cells. Loss of FOXA1 expression was associated with upregulation of 1358 genes including CD274 (PD-L1) and other interferon response genes, and downregulation of 2187 genes. d Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) identified the interferon alpha and gamma pathways as the top two gene sets altered following FOXA1 knockout in UM-UC-1 bladder cancer cells. e FOXA1 mRNA expression was significantly negatively correlated with CD274 (which encodes PD-L1) mRNA expression in the TCGA bladder cancer cohort (two-sided Spearman correlation). f FOXA1 regulon activity profiles for 404 samples in the TCGA BLCA cohort sorted by FOXA1 regulon activity (left), molecular subtypes and CD274 gene expression (right). g Kaplan-Meier plot of the bladder TCGA cohort13 showed that disease-specific survival (DSS) was significantly associated with positive vs. negative FOXA1 regulon activity status (Log-rank p-value = 0.01). Numbers indicate patients in each group and, in curved parentheses, deceased patients. h Correlation between FOXA1 and CD274 mRNA expression across 24 cancer types from the TCGA analysis showed that the most significant inverse association between these genes was observed in bladder cancer.