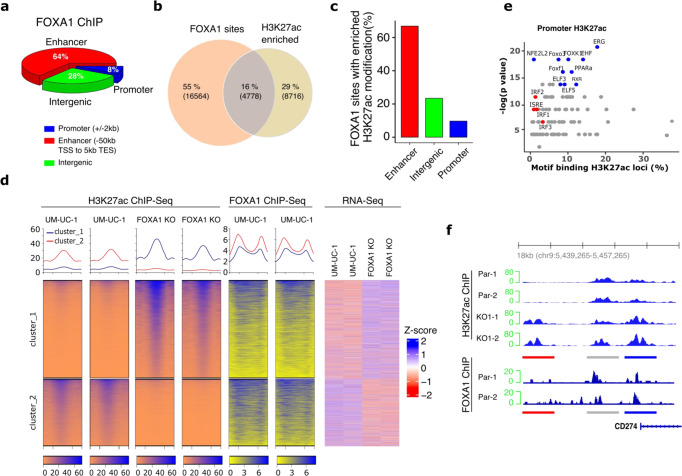
Fig. 6. FOXA1 knockout was associated with widespread enhancer and promoter epigenetic reprogramming in bladder cancer cells.
a ChIP-Seq was performed in duplicates using chromatin extracted from UM-UC-1 parental and UM-UC-1 FOXA-1-KO cells. 21,766 FOXA1 binding sites were identified in the ChIP-Seq data by MACS2 (FDR < 0.001). Genomic regions where FOXA-1 binding sites were located were then annotated as promoter (2 kb+/− transcriptional start site—TSS), enhancer (between −50 kb from TSS and 5 kb after transcriptional end site—TES), or intergenic (other sites). b Integrated ChIP-Seq analysis of FOXA1 binding sites and H3K27ac revealed 14971 differentially modified H3K27ac loci enriched in either parental UM-UC-1 cells or those with FOXA1 KO (55% were unique FOXA1 binding, 29% were histone H3K27ac enriched sites, and 16% overlapping sites, defined as within 5 kb), c The majority of the overlapping sites were in enhancer regions with fewer sites in the intergenic or promoter regions. d Cluster analysis of the H3K27ac-modified enhancer regions enriched in either the parental UM-UC-1 cells or the isogenic FOXA1-KO cells (left), FOXA1 binding coverage around the same region (middle), and the expression of genes associated with these sites (right). The number of clusters was defined by kmean (k = 2) in H3K27ac enriched peaks. All analyses were performed in duplicate. e Known motif scanning of the sites enriched with H3K27ac modification in the gene promoter regions identified the top 10 significantly enriched motifs (blue dots) and motifs of interferon-regulatory factors (IRF) or interferon-sensitive response element (ISRE) (red dots). f Increased acetylation of CD274 gene regulatory elements including an upstream enhancer (red line region) and the proximal promoter region (blue line) in FOXA1-KO versus parental UM-UC-1 cells (top). For reference, unchanged peaks are shown (grey line). FOXA1 binding sites were also identified in the promoter region of CD274 gene by ChIP-Seq (bottom).