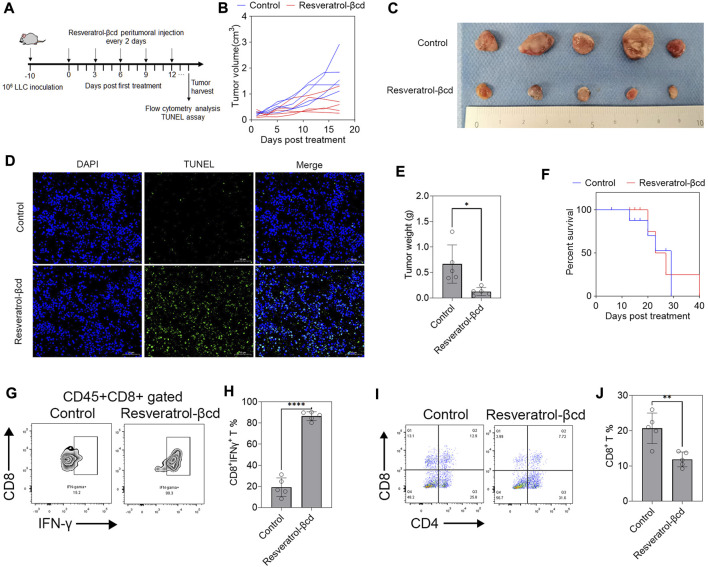
FIGURE 2.
Resveratrol-βcd activates tumor-infiltrating CD8T cells against lung adenocarcinoma. (A) A graphical representation showing the timeline of in vivo experiments. A total of 106 LLC cells were inoculated into the right flank of mice. Approximately 10 days post-inoculation, the tumor volume reached around 300 mm3 and drug administration began. The first day of drug administration was recorded as Day 0 post-treatment. Paratumoral injections were administered every 2 days until reaching the humane endpoint. (B) Resveratrol-βcd, equivalent to 5 mg/kg resveratrol, was injected adjacent to the tumor every 2 days, while the control group received the same amount of βcd. The results showed significant inhibition of tumor growth in the treatment group (n = 5). (C) Typical images of tumors after the mice were sacrificed 17 days after treatment. (D) A typical graph of TUNEL analysis of tumor apoptosis 17 days after treatment. Scale bar = 50 μm. (E) The mean tumor masses after dissection were 0.126 g and 0.666 g in the treatment and control groups, respectively. Error bar = mean ± S.D., n = 5; *p = 0.014. (F) Survival curves of the resveratrol-βcd and control groups. All mice in the control group reached the humane endpoint at 29 days post-treatment, compared to 40 days in the resveratrol-βcd group. n = 5. (G) Typical flow cytometry diagram of CD8T activation in tumors. The cells were CD45+CD8+ gated. (H) CD8T cell activation in the treatment and control groups. Error bar = mean ± S.D., ****p < 0.0001. (I) Typical flow cytometry diagram of CD4T and CD8T cells in tumors. The cells were CD45+ gated. (J) The ratio of CD8T in the treatment and control groups. Error bar = mean ± S.D., **p < 0.01.