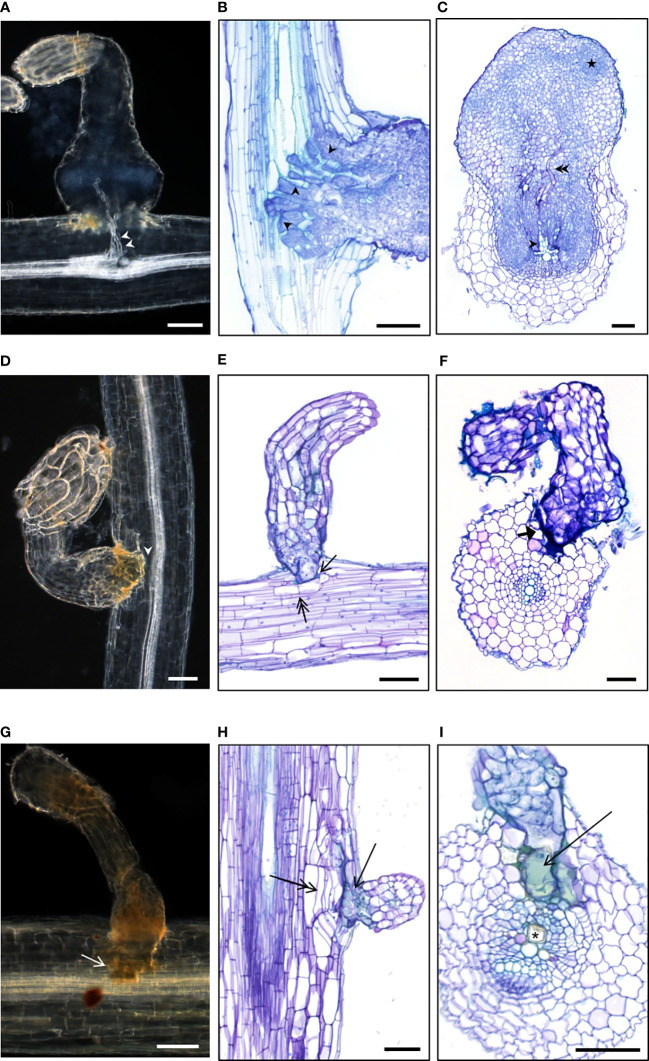
Figure 5.
Cytological study of compatible and incompatible attachments revealed various cellular resistant mechanisms (A–C) Compatible attachments of susceptible wild H. annuus or cultivated H. annuus with established vascular connections. Xylem vessels indicated by white arrowheads in (A) and black arrowheads in (B) Phloem vessels indicated by double black arrowheads in (C) The star indicates Orobanche dividing cells preparing bud development. (D–I) Incompatible attachments of resistant wild Helianthus species. (E, F) no or few cortical cell divisions (double arrow in E); phenolic compounds at the basis of the haustorium (arrow in E); thick cell wall surrounding the haustorium (thick arrow in F). (H, I) cortical cell division under or around the haustorium (double arrow in H), phenolic compounds (arrow in H, I), mucilage deposition in the host xylem vessel (asterisk in I). The pictures were taken from various accessions: (A) H. annuus #649; (B) sunflower control XRQ; (C) sunflower control 2603; (D) H. annuus #833; (E) H. exilis #2601; (F) H. bolanderi#584; (G) H. annuus #833; (H) H. grosseserratus #290; (I) H. annuus #833. (A, D, G) Whole cleared root samples with attachments. (B, C, E, F, H, I) Sections of included root samples with attachments, stained with toluidine blue O. Bars = 100 µm.