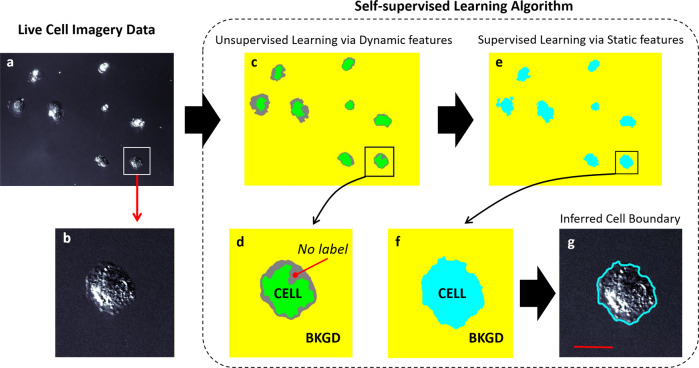
Fig. 2. Overview of the automated self-supervised learning algorithm.
a The contrast enhanced DIC image of several and b a single highlighted MDA-MB-231 cell illustrates the range of intensities inherent within the cells. (20X objective). c, d Unsupervised learning via FD: high threshold FD is used to select only those pixels exhibiting the highest displacement magnitudes and labels them as ‘cell’ (green pixels). Similarly, low threshold FD is used to identify pixels with a much wider range of displacement magnitudes than the high flow regime. The lowest displacement magnitude pixels are labeled ‘background’ (yellow pixels). Pixels that exhibit FD in between these regimes remain unlabeled (gray pixels). e, f Supervised learning via self-labeled training data. The self-labeled pixels (green and yellow) are then used to generate static feature vectors, which are in turn used to train the classifier model. g The blue outline is the resulting segmentation which outlines all pixels classified by the FD trained model as ‘cell’ and is also overlaid on the image in b. This process is repeated at every time step, thereby using the most recent imagery to update the training data. Scale bar: 25 µm (20X objective, time increment: 300 s).