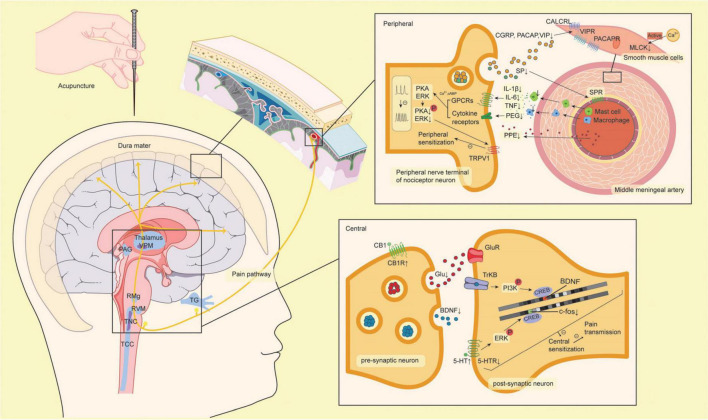
FIGURE 3.
The mechanism of acupuncture protecting from neuroinflammation and neuronal sensitization of migraine. The yellow line through the brain represents the pain pathway. The factors are shown with up and down arrows, which represent up- or down-regulation from acupuncture. The pathways with minus on the line are inhibited by acupuncture. 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HTR, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; TrkB, tropomyosin kinase B; CB1, cannabinoid 1; CB1R, cannabinoid 1 receptor; CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide; CALCRL, calcitonin receptor-like receptor; COX2, cyclooxygenase-2; CREB, cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Glu, glutamate; GluR, glutamate receptor; GPCRs, G protein-coupled receptors; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-6, interleukin-6; MLCK, myosin light chain kinase; PACAP, pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide; PACAPR, pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide receptor; PAG, periaqueductal gray; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKA, protein kinase; PPE, plasma protein extravasation; RMg, raphe magnus nucleus; RVM, rostroventromedial medulla; SP, substance P; SPR, substance P receptor; TCC, trigeminocervical complex; TG, trigeminal ganglion; TNC, trigeminal nucleus caudalis; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; TRPV1, transient receptor potential vanilloid 1; VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide; VIPR, vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor; VPM, ventro-posterior medial thalamic nucleus.