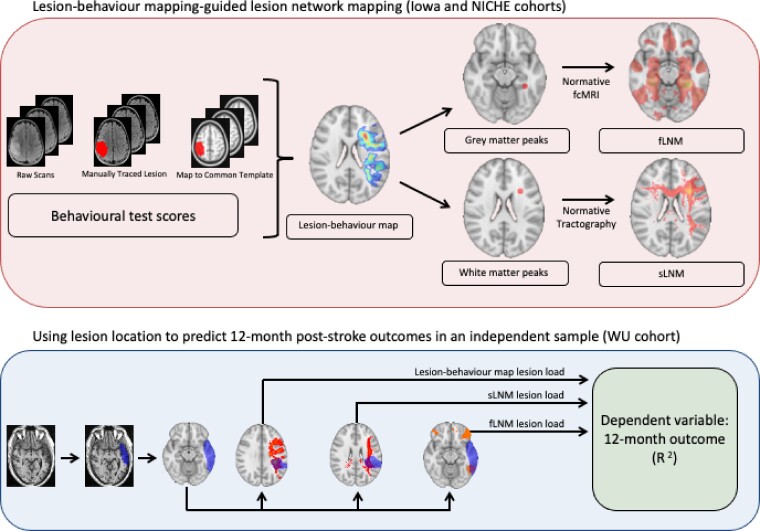
Figure 1.
Schematic of approach. Multivariate LBMs were generated from sparse canonical correlation analysis based on lesion locations (i.e. voxel lesion status) and behavioural measurements. Data from the Iowa and NICHE cohorts were used to generate LBMs for cognitive and motor functions, respectively. These statistically-weighted maps were used to identify seed regions-of-interest for structural and functional lesion network mapping (LNM), which explore the structural and functional brain networks associated with regional peaks in the white and grey matter from each LBM, respectively. Then, for each patient in the WU cohort, we summed the voxel intensities from the LBM and structural and functional LNM results that also appeared in the patient's lesion mask to generate lesion load scores. The 12-month post-stroke outcome for each domain in the WU cohort was predicted from the lesion load scores. We examined the separate and combined effects of these predictors.