Figure 5.
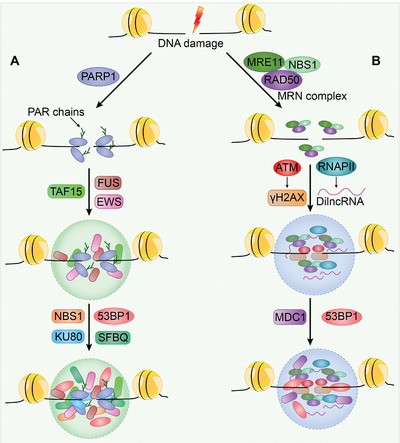
Model of DNA repair foci. A) Poly(adenosine 5’‐diphosphate‐ribose) polymerases (PARP)‐mediated DNA repair. Upon DNA break formation, PARylation is induced by PARP to recruit fused in sarcoma (FUS), Ewing's sarcoma oncoprotein (EWS), and TATA‐box binding protein associated factor 15 (TAF15), which drive DNA damage condensate assembly. DDR factors including ATP‐dependent DNA helicase II subunit 2 (KU80), Nijmegen breakage syndrome protein 1 (NBS1), p53 binding protein 1 (53BP1), and splicing factor proline and glutamine‐rich (SFPQ) are then attracted to the DNA repair foci. B) Meiotic recombination 11 (MRE11)‐RAD50 double strand break repair protein (RAD50)‐NBS1 (MRN) complexes formed repair foci. The MRN complexes recruit the apical protein kinase ATM for H2A histone family member X (H2AX) phosphorylation (γH2AX). Meanwhile, RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) is also recruited to transcribe damage‐induced long noncoding RNAs (dilncRNAs). Consequently, these molecules drive the molecular crowding of DNA repair‐related proteins, including the mediator of DNA damage checkpoint protein 1 (MDC1) and 53BP1, for the assembly of DNA repair foci.
